Current rapid prototyping techniques have greatly influenced the design of products and processes, but their accuracy and selection of appropriate materials are frequently constrained. Furthermore, the existing techniques are not very similar to standard production procedures.
It is crucial to create a part in a suitable material when the part being designed needs to undergo extensive performance and failure testing. In the 4.0 industrial era, the subtractive approach of CNC machining was comparatively more reliable and accurate. However, even in 2025, CNC machining is still the industry standard for accuracy, speed, and material adaptability when producing prototypes.
Yet, CNC machining is a great tool for quick prototyping. In this blog, you will learn how a revolutionary technology known as CNC-RP is the best choice. The purpose of this blog is to explain CNC machining to create functioning prototypes in a variety of materials. So, let's dive deep into it.
1. CNC Machining Capability
CNC Machining is one of the most trustworthy processes of manufacturing. It is unbeatable in speed, accuracy, and cost efficiency, and offers machining services to a wide range of materials. In the smart manufacturing era, CNC machining performance is enhanced by its simulation with digital technology. Here are some CNC machining features.
● Precision & Accuracy
CNC is a subtractive process that requires a line of sight for the cutting tool, unlike other RP methods. CNC can create parts in a wide array of the most commonly used materials with very high accuracy. Typically, rough machining can achieve +/- 0.002" and finish machining can achieve +/- 0.0005", a combination that is not commonly seen in other commercial RP processes.
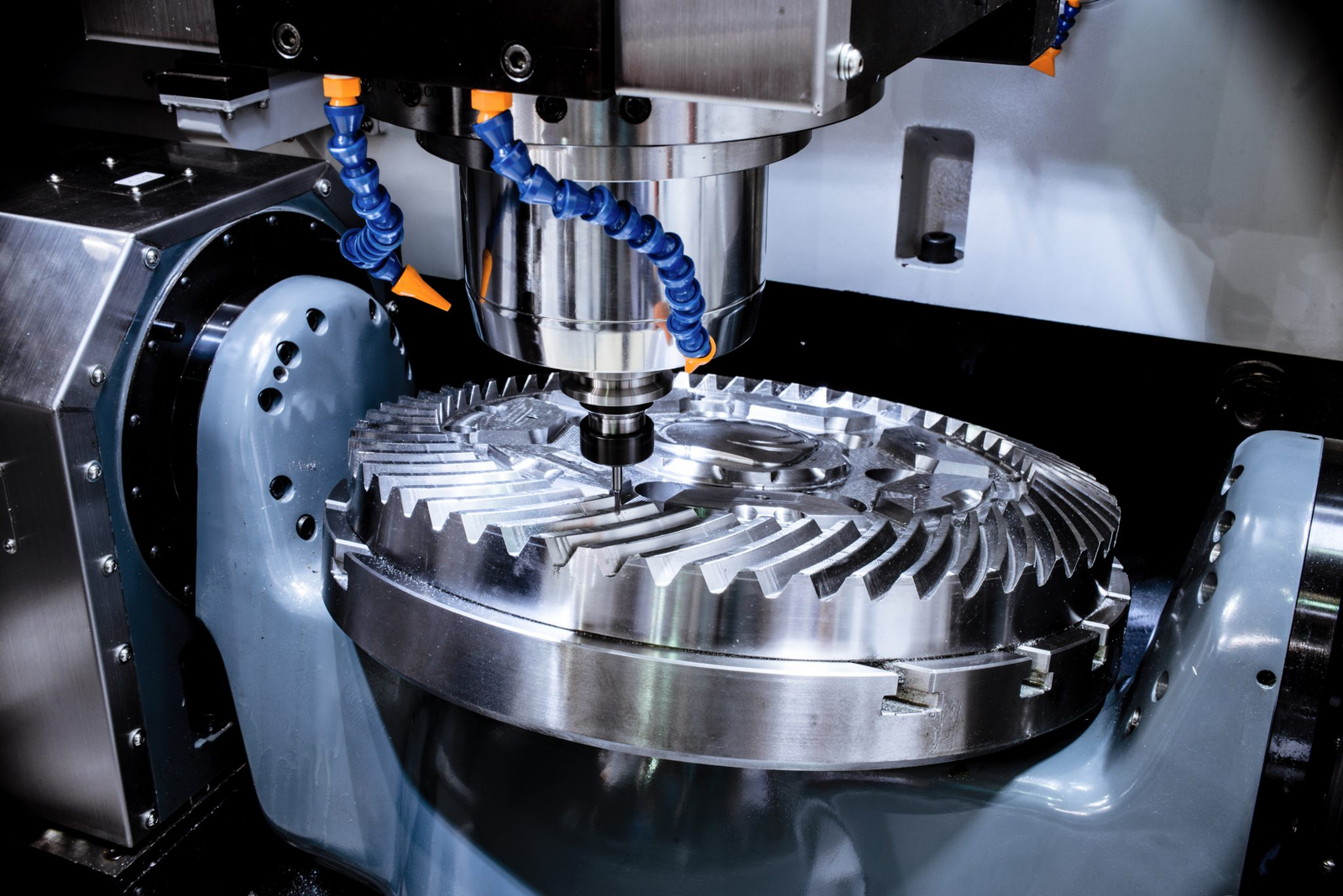
The level of precision is very crucial in many industries like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive. The minor deviation can cause major issues with safety and machining performance. Even in complex products with intricate features, CNC machines can retain geometric consistency and exceptional surface finishes due to the integration of constant input from sensors and (3-, 4-, or 5-axis) multi-axis control.
Furthermore, another distinguishing feature of CNC machining is repeatability. Many thousands of identical parts with the same specifications and finish quality can be manufactured once a digital model has been developed. Because of its uniformity, CNC machining is dependable and effective for mass production and prototypes, reducing the need for rework and quality inspection time.
● Material Versatility & Real-World Behavior
CNC (computer numerical control) machining has practically become a necessity for industrial companies nowadays. CNC machines can achieve high levels of accuracy and precision that are not achievable with conventional manufacturing equipment. CNC lessens vibration during traditional machining. There is a vast range of material available that shows amazing versatility in the real world. Here are a few materials.
1. Metals
CNC machining is still the best option for creating metal parts because of its material diversity, surface finish quality, and dimensional accuracy.
● Stainless Steel
AISI 316 SS is an important alloy with remarkable properties that can be utilized in severe and demanding conditions. A few industries that commonly use AISI 316 stainless steel are the aerospace sector, nuclear plants, food and medical industries, oil refinery pipes, and water filtering systems.
Using a milling cutter with uncoated carbide inserts, Ernández et al. milled AISI 304 steel and investigated how machining factors affected hardness and SR. They found that increasing cutting speed and feed rate had the least impact on AISI 304 steel's hardness, but that cutting speed had a substantial impact on SR, and that higher cutting speeds and smaller feed rates produced superior surface finishes.
- Aluminum
Aluminum's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior machinability, and inherent resistance to corrosion make it one of the most popular materials for CNC machining. The most widely used of them are aluminum 6061 and aluminum 7075.
2. Composites
Composite materials are now used more widely in the majority of the top manufacturing industries. The most important option for producing components with tighter tolerances is machining. Many engineering domains use the second generation of hybrid composites, which serve as superior substitutes for a variety of materials.
3. Polymer
Prototypes are frequently made from CNC-machined polymers since they can mimic the shape and functionality of finished plastic parts without the need for molds. Quick part evaluation, iterative design modifications, and performance validation prior to injection molding mass production are all made possible by this.
| Material | Properties | Why it useful |
| Carbon Fiber Composite | It is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, and offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. | It offers good mechanical properties, high machinability, with lightweight material. |
| ABS Polymer | Shaping carbon fiber components with intricate geometries provides control and accuracy in CNC machining. | It is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, and offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. |
| Stainless steel (AISI 304, 316) | Strong, resistant to corrosion, and perfect for aerospace and medical applications | It is a fundamental material in many sectors due to its strength, toughness, and ease of processing. |
| Aluminum ( Al 6061, 7075) | High machinability, corrosion resistance, and lightweight | In general, aluminum is a ductile, soft metal that is easy to machine. |
| Titanium (Ti- 6Al-4V) | High strength-to-weight ratio, utilized in biomedical and aerospace | It has historically been challenging to machine because of its high reactivity and limited thermal conductivity, but contemporary CNC tools, coatings, and cooling methods have greatly increased its machinability. |
● Speed & Iteration Capability
The study emphasizes that CNC machining may be used efficiently for rapid prototyping, allowing producers to go from CAD model to real part much more quickly than many conventional techniques. The "lead time" is reduced for one-off or small batch manufacturing since setup (tooling, fixture, programming) stays the same.
Turnaround is quicker since the technology allows for short production runs without requiring costly molds or drawn-out tooling procedures. According to the report, one of the main benefits of CNC machining is its support for rapid iteration, which allows you to make changes to a design and quickly have an updated version manufactured.
● Cost Efficiency for Low to Medium Volume & Prototype Runs
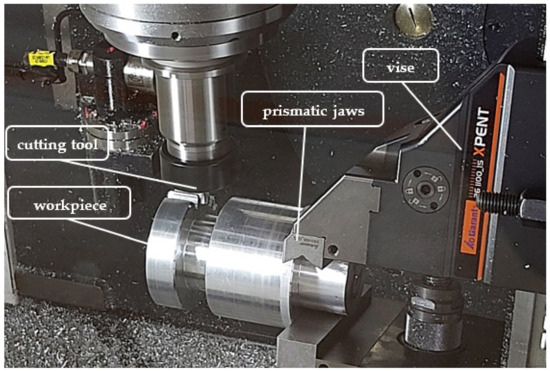
Industrial sectors are concentrating on high production at low cost in today's competitive environment. In particular, manufacturing sectors are focusing on producing a range of things in large quantities.
Rapid, low-volume fabrication without a significant upfront investment is made possible by CNC machining, which provides a very cost-effective way to produce prototypes since it does not require the costly fixed gear and molds needed for injection molding or other similar techniques. Faster iterations are made possible by its high precision and strong material versatility, which also lowers waste and post-processing costs.
When appropriately planned, the cycle time from CAD to the final product is minimal. Studies have demonstrated, for instance, that in small-series machining situations, realistic cost estimates may be obtained by modeling component complexity, material selection, and machining time.
Additionally, CNC machining works well for functioning metal prototypes where precision, durability of the material, and surface polish are essential. For industrial-grade prototypes, many additive or low-cost technologies cannot achieve these requirements.
2. Emerging Technologies in Manufacturing
There are some emerging technologies that are reshaping the manufacturing world. It is changing the way of production, designing products, and prototype manufacturing. Here are some latest technologies you will need to know.
1. Artificial Intelligence
The manufacturing industry could undergo a significant transformation because of recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning (ML), which offers sophisticated analytical tools for handling the massive volumes of manufacturing data produced, or "Big Data."
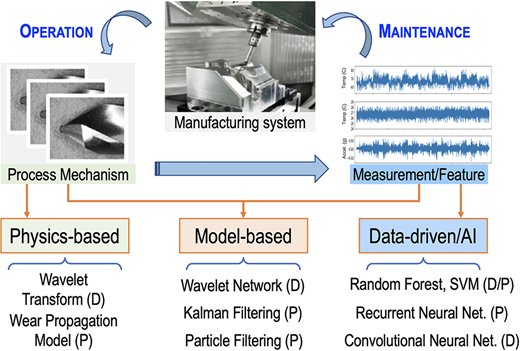
Application of AI in Manufacturing Analysis
The utilization of AI tools in process monitoring, diagnostics, and prognostics has grown more widespread due to the abundance of data coming from sensors, equipment, and processes. Traditional ML techniques extract pertinent features from high-quality data.
Due to numerous uncertainties and interdependencies, factory operations are extremely nonlinear and chaotic. Therefore, the use of AI-based diagnostics to create categories and link data to appropriate fault kinds and severity levels has become widespread.
2. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
The process of layer-by-layer deposition of materials to create parts, also referred to as additive manufacturing or three-dimensional (3D) printing, has been booming as a fabrication technique in recent years and can now produce complex geometries to utilize as production molds, assembly fixtures, and models.
Although there has been an increasing demand for using this technique for the direct manufacturing of finished parts, it is still primarily restricted to single-material production, which may limit the designs' ultimate performance. In addition to integrating disparate materials, the next generation of 3D printing will also include active components to provide functionality that was previously unattainable.
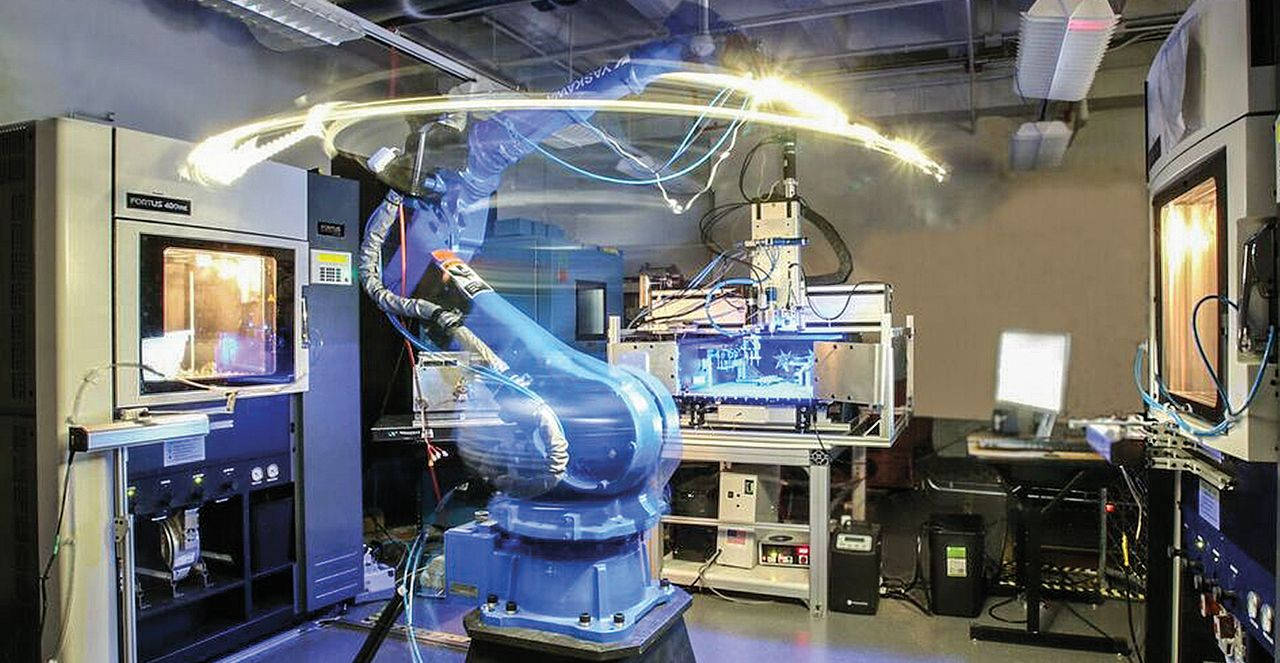
3. Robots in Advanced Manufacturing
Automation and robotics have drastically changed (CNC) machining processes, increasing efficiency, accuracy, and production. components, produced parts, and raw materials are loaded and unloaded onto CNC machines by robots. Their ability to manage large, heavy parts effectively lowers the need for physical labor and lowers the possibility of accidents.
Additionally, robots can be employed in CNC machine centers to carry out operations including workpiece placement, part inspection, and automatic tool replacement methods. CNC machining cells can incorporate automation technologies, such as Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) techniques and in-line monitoring methods, to improve accuracy and lower scrap and rework in machining operations.
In order to forecast maintenance, optimize machining settings, and boost efficiency in general, these systems gather real-time data on process variables and machine tool operation.
4. Sustainable Manufacturing
Manufacturing environments face a variety of challenges, including social, economic, environmental, and technical ones. Environmental challenges include things like climate change and the depletion of natural resources. It is another necessary component in production.
In sustainable manufacturing, goods are manufactured in a way that conserves energy and other resources while minimizing adverse environmental effects. Due to pressure from consumers and authorities to provide environmentally friendly products, sustainability assessment is swiftly becoming an unavoidable concern for manufacturing companies.
To ensure a sustainable and clean energy future, manufacturers ought to be able to evaluate and compare current manufacturing technologies based on sustainability. Eliminating waste, satisfying consumer needs for environmental performance, and reducing energy and material costs for greener products are the goals of sustainable production, also referred to as green manufacturing.
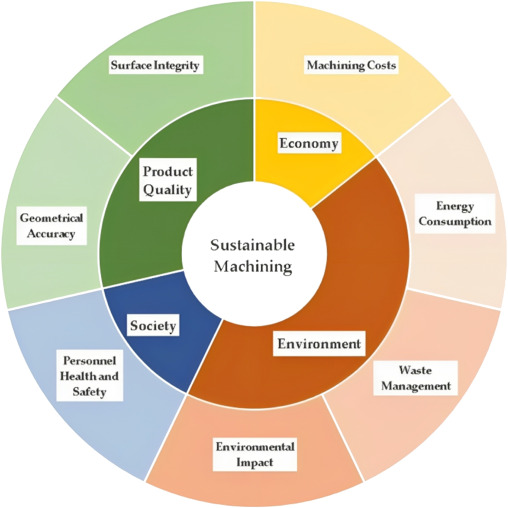
Sustainable Machining
5. Digital Twin Technology in Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is based on the digitization of industrial systems. Digitalization and the creation of digital twins in manufacturing have been made possible by recent technological developments, including smart sensors, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI). According to a recent Gartner poll, 75% of IoT-implementing firms either currently employ digital twins or intend to do so in the coming year.
The idea of a digital twin could be crucial to the realization of smart manufacturing. The idea and its application in actual manufacturing systems, however, are still quite unclear, particularly for medium-sized companies.
3. CNC Fulfill Manufacturer Modern Demands
In this 4.0 industrial era, manufacturers demand accuracy, precision, sustainable manufacturing, cost efficiency, quick turnaround to stay competitive in the market. Thus, CNC accomplished all these manufacturers' needs by automation, applying advanced materials and digital integration.
1. Speed and Efficiency
CNC automation has increased the speed and efficiency of CNC machines. Robotic loading systems, real-time feedback sensors, and automatic tool changers that increase operating efficiency. It lowers the need for employee intervention.
2. Cost Efficiency
The CNC machining process is highly cost-efficient. It offers the best possible balance between price, quality, and speed. It is one of the most cost-effective manufacturing methods on the market today because it lowers tooling costs, decreases waste by sustainable production, and guarantees consistent, high-quality output, whether for small-batch production or working prototypes.
3. Sustainable manufacturing
Optimizing CNC machining parameters is an essential production technique that seeks to raise the effectiveness, caliber, and affordability of CNC machining processes. Manufacturers can improve the surface smoothness of machined items, minimize tool wear, and shorten cycle times by fine-tuning machining settings. Optimization of sustainable CNC machining operations can be achieved by taking into account a number of factors, including:
- Material Selection
- Cutting Parameters
- Tool Selection
- Waste management
- Tool Lubrication and Cooling
4. Integration with Digital Technology
Manufacturing in the era of Industry 4.0 is quickly moving toward data-driven and digitally connected processes. A key component of this change is CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, which integrates with cutting-edge digital technologies, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), digital twin systems, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Throughout the manufacturing cycle, these technologies optimize CNC performance, increase precision, and facilitate predictive decision-making.
4. CNC Machining Comparison with Other Trending Technologies
1. CNC Machining VS 3D Printing
Comparison:
- 3D printing adds material (additive process), whereas CNC machining subtracts material (subtractive process).
- Particularly for metals like steel, titanium, and aluminum, CNC provides improved material strength, surface polish, and dimensional precision.
- But for quick low-strength prototypes and intricate geometries, 3D printing is better.
Verdict:
- CNC machining works better than 3D printing for working prototypes or production-grade products that need strength, accuracy, and tight tolerances.
2. CNC Machining Vs Robotic and Automated Manufacturing
Comparison:
- Although robotic automation (such as flexible cutting systems or robotic arms) increases speed and reproducibility in large production, it frequently falls short of CNC's precise machining accuracy.
- CNC machines can automate part handling and tool changes, resulting in hybrid systems that balance productivity and accuracy.
Verdict:
- The conclusion is that full robotic automation is more effective for repetitive, large-scale production, but CNC machining is still superior for high-precision, small-batch, or custom metal products.
3. CNC Machining Vs AI-Driven Smart Manufacturing
Comparison:
- Machine learning is used in AI industrial systems for optimization, quality assurance, and predictive maintenance.
- AI-enabled CNC machining (such as adaptive toolpath correction or real-time sensor feedback) increases productivity and decreases downtime.
Verdict:
- CNC and AI technologies enhance one another rather than compete. Industry 4.0 currently includes smart CNC equipment that performs better than conventional manual machining.
4. CNC Machining Vs Sustainable Manufacturing

Comparison:
- When contrasted with additive methods, CNC machining is more energy-intensive and produces more material waste.
- However, innovations in CNC technology, such as hybrid additive-subtractive machining, coolant recycling, and toolpath optimization, make it more environmentally friendly.
Verdict:
- Although 3D printing might produce less waste, higher process control and metal recycling from CNC milling help bridge the sustainability gap.
6. Conclusion
Precision, dependability, and efficiency remain key components of CNC machining in the current, quickly changing manufacturing environment. In terms of accuracy, repeatability, and material diversity, CNC machining is still superior to developing technologies like additive manufacturing and hybrid systems, which offer flexibility and design freedom.
In order to achieve smarter and more sustainable production, modern businesses are integrating CNC more and more into the Industry 4.0 ecosystem. This includes merging CNC with digital twins, IoT monitoring, and AI-driven optimization.
In the end, the decision is based on the particular application:
- CNC machining continues to be the most reliable and affordable choice for medium-to-large batch manufacturing with high precision and tighter tolerances.
- Additive manufacturing or hybrid technologies provide special benefits for lightweight lattice structures, complex geometry, or rapid prototyping.
The most competitive companies will be those who strike a balance between creativity and precision, utilizing the established advantages of CNC machining while embracing digital transformation for the future of smart manufacturing, as research and technology continue to progress.






