Are you struggling to choose between CNC machining and die casting for your next project? This decision affects cost, quality, and timelines.
CNC machining offers unparalleled precision and material versatility, making it ideal for complex parts and small batch sizes. Die casting, on the other hand, is more cost-effective for large quantities and provides fast production once molds are ready.

CNC machining precision vs die casting efficiency
Choosing the right process depends on your project's specific requirements, including budget, volume, and quality needs. Let's dive deeper into the factors influencing this choice.
What Are the Key Differences Between CNC Machining and Alternative Manufacturing Methods?
Not sure where CNC machining fits in the manufacturing landscape? You're not alone—many struggle to understand its unique benefits.
CNC machining is superior for high-precision tasks, offering versatility with materials ranging from metals to plastics. Its ability to produce smooth surfaces minimizes post-processing.
Comparison of manufacturing methods
When exploring alternative methods like die casting or 3D printing, consider their strengths and limitations. Die casting excels in large-scale production due to quick mold setups post-preparation. In contrast, 3D printing’s slower pace suits prototype development. CNC machining strikes a balance, excelling in both small and varied-material orders.
How Does Material Selection Impact Your CNC Machining Project Cost and Timeline?
Materials matter more than you think in CNC machining. Miss a step here, and costs can spiral.
The choice of material can significantly affect both the timeline and the cost of CNC machining. CNC is versatile, handling metals, composites, and plastics, factoring into costs based on hardness and availability.

Selecting materials wisely involves balancing your needs against material properties and machining complexities. Denser materials require more machining time, increasing costs. Additionally, some materials may shorten tool life, influencing replacements and thus costs.
When Should You Choose CNC Machining Over Injection Molding?
Choosing between CNC machining and injection molding can be tricky. However, get it wrong, and you'll see rising expenses.
CNC machining is ideal for low-volume, high-complexity projects where part accuracy takes precedence. The opposite applies to injection molding, making it fit for mass production post-mold creation

Choosing between CNC and injection molding
Injection molding involves significant upfront tooling costs but thrives in larger production runs. CNC machining doesn't require this investment, offering flexibility for changes and small to medium quantities without mold costs. Use CNC for parts needing design revisions or a range of material properties.
What Production Volumes Make CNC Machining More Cost-Effective?
Wondering if your production volume justifies CNC machining? This is crucial for cost-effectiveness.
CNC machining is most cost-effective for complex, low-volume projects or when frequent design changes are needed. As production volume increases beyond medium scales, methods like die casting may become more economical.

CNC cost-effectiveness by volume
Understanding when CNC becomes less favorable involves comparing initial tooling costs and material use. High setup costs in casting processes demand larger volumes for pay-off. Opt for CNC for precision-oriented parts without the need for extensive upfront investment in tools.
How Does Surface Finish Quality Compare Between Different Manufacturing Methods?
Quality finish impacts product aesthetics and functionality. Select poorly, and you’ll compromise either.
CNC machining produces superior surface finishes due to precise cutting, minimizing post-work refinements. 3D printing often struggles with rough finishes due to layering, while die casting can produce smooth surfaces but often requires subsequent processing.
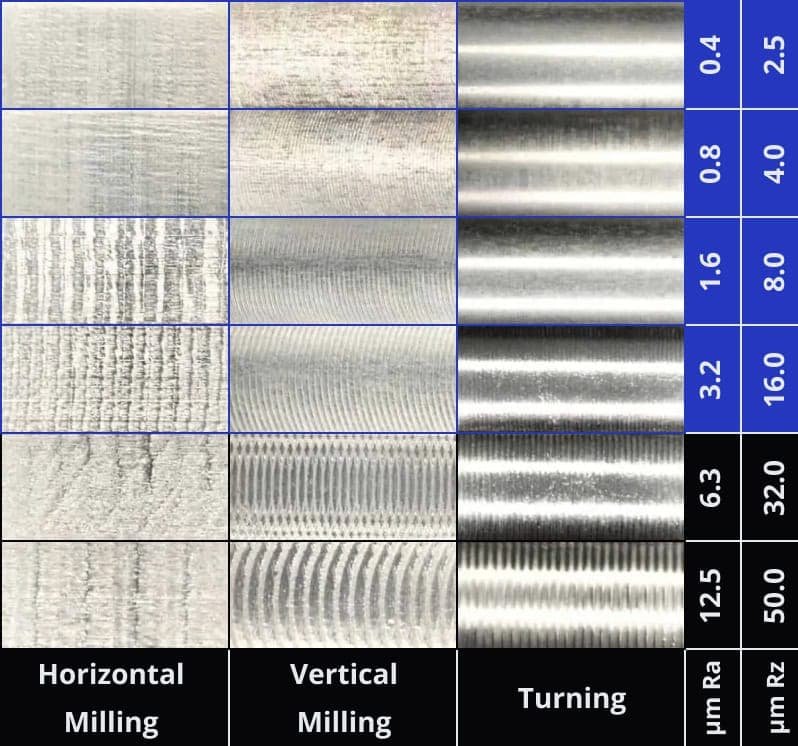
The decision hinges on project needs. CNC's precise tooling reduces burrs and finishing scratches, ideal for aesthetically focused or functional parts. Consider die casting when large, simple geometry parts and consistent results are necessary.
Conclusion
CNC machining and die casting serve distinct purposes. Your choice should consider precision, volume, and material needs. CNC machining and die casting serve distinct roles in manufacturing. CNC is best for precision, complexity, and materials flexibility, while die casting fits large-scale, cost-driven scenarios. Understanding your project's unique requirements, from volumes to material needs, guides the right choice, ensuring quality and cost-efficiency.





