
Introduction
Acrylic stands as a widely utilized clear plastic within CNC systems. Its popularity arises from its exceptional properties, surpassing those of materials like polycarbonate and glass. This comprehensive guide delves into the realm of CNC acrylic machining, unraveling the “hows” and “whys” behind its prominence. From suitable CNC processes to invaluable machining tips, we explore the nuances of acrylic production.
Understanding Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic, also known as Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), is a thermoplastic material with remarkable attributes. This versatile plastic retains its fundamental characteristics even when melted and reshaped. Unlike some other clear plastics, acrylic does not discolor after prolonged exposure to sunlight. It stands as an excellent alternative to glass in various applications, finding extensive use in industries like automotive and test and measurement.
Key Properties of Acrylic:
Surface Hardness: Acrylic’s density ranges from 1.17g/cm3 to 1.20g/cm3, imparting remarkable surface hardness. It outperforms other transparent polymers in scratch resistance thanks to its excellent dimensional stability. This toughness results in a highly durable and long-lasting material.
UV Stability: Acrylic’s strong UV resistance ensures durability under prolonged sunlight exposure. This feature is vital for outdoor applications, particularly in open-air settings.
Transmittance: Thanks to its refractive index of 1.49, acrylic allows for exceptional light transmittance, up to 92%. This surpasses glass and other plastics, ensuring optical clarity. Its environmental stability is perfect for various outdoor applications.
Chemical Resistance: Acrylic exhibits impressive chemical resistance, unaffected by typical laboratory aqueous solutions. It withstands cleaners, alkalis, and detergents, and dilutes inorganic acids without harm. This quality makes acrylic a reliable choice for fluidic and medical manifold applications, free from chemical reactivity concerns.
High Impact Resistance: With its remarkable resilience to shocks and impacts, acrylic has 17 times the impact resistance of ordinary glass, greatly lowering the possibility of breaking.
Temperature Resistance: Acrylic has a low melting point (between 102 and 1220 degrees Celsius), however machined acrylic is quite resistant to temperature changes. Diffusion bonding and other forms of heat treatment are made possible. This property of the material also makes it perfect for applications in the medical and food industries.
Lightweight: When compared to a regular glass of the same size, Plexiglass weighs only half as much. Because of its low density, CNC machining acrylic is a simple process.
CNC PMMA Machining Techniques
Acrylic lends itself nicely to a variety of machining techniques. The technique used is often determined by the requirements provided by the customer. Depending on the intended product design, one or more of the following processes may be used in the manufacture of acrylic.
CNC Acrylic Milling
acrylic milling (Reference)
This method of CNC machining acrylic provides excellent chip control and requires the removal of acrylic material. The acrylic sheet or other workpiece is fed through the CNC machine and then cut using the appropriate cutting tool. It moves in the same direction as the cutting instrument while it does this. This method shines when used for the milling of intricate geometries. CNC machining of acrylic is best accomplished using cutting tools that feature edge rake angles and rotating multi-points. The acrylic milling machine shop can do a variety of cuts, from shallow to deep to peripheral, with the help of this cutting tool.
CNC Acrylic Turning
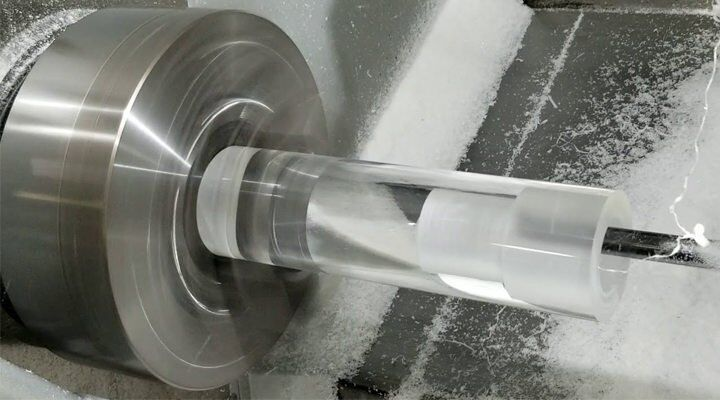

This method of producing acrylic products requires cutting away at a rotating piece of acrylic. In contrast to CNC milling acrylic, the cutting tool utilized here only has one axis of rotation. During this method of CNC machining acrylic, the machine passes the cutting tool in a straight line over the surface of the acrylic workpiece. It works its way around the item, cutting away excess material until the desired form is achieved. Thread cutting, boring, grooving, and facing are only some of the CNC acrylic turning’s machining capabilities.
CNC Acrylic Drilling
In CNC acrylic drilling, multi-point drill bits are employed to create cylindrical holes in acrylic material. The CNC tool feeds these rotating drill bits perpendicularly to the acrylic surface, resulting in vertical holes of matching bit diameters. Specialized machine setups enable angular drilling operations. This versatile process encompasses reaming, tapping, countersinking, and counterboring. While it’s efficient and straightforward, it’s worth noting that CNC drilling may yield less-than-ideal surface finishes in some cases.
CNC Acrylic Engraving

CNC acrylic engraving is a precision machining technology that uses a computer to mechanically engrave patterns, symbols, or artwork onto acrylic materials. Without the need for workholding, this approach ensures reliable, precise outcomes every time. Though it’s incredibly effective, it can be pricey because to the need for expensive machinery. To engrave acrylic is similar to milling, with a different cutter being used. Useful in both commercial settings and the realm of art, it has widespread popularity. Precision computer numerical control machines have made it possible to carve complex patterns into acrylic sheets. When the grooves are filled with paint, they become more visible.
CNC Acrylic Cutting
The method of CNC acrylic cutting entails directly cutting an acrylic workpiece by making contact with the cutting tool. While the actual machining is done by hand, computer programs decide the cutting tool’s course. This suggests that CNC cutting of acrylic is done by portable devices using automation. During the machining process, the CNC control equipment receives the command and uses the provided program to carry out automated cutting. These solutions are often utilized in small organizations and educational institutions since they are reasonably priced. It is essential to have the best CNC system to guarantee high-quality cuts because it cuts quite quickly.
Tips for Successful CNC Acrylic Machining
When working with a CNC machine, acrylic is a great material choice. CNC acrylic is useful for a broad range of applications. You need to know a few things, however, to make sure the manufacturing goes well. Using the following guidelines, your acrylic CNC cutting project will end up looking great.
I. Choose the Right Acrylic Material
Select the acrylic material that suits your specific needs. Acrylic varies in transparency, melting points, and rigidity. This versatile material is compatible with various CNC machining processes.
II. Select the Proper Cutter
Ensure your CNC machine has sharp and robust cutter edges to prevent acrylic from melting during cutting. Avoid cutters previously used with metals as they may have jagged edges. Carbide cutters are often preferred for acrylic machining. Single-flute cutters maximize chip clearance and prevent heat buildup.
III. Use the Correct Bits
Opt for carbide drill bits when drilling acrylic. O-Flute End Mill Bits designed for acrylic cutting and drilling are a reliable choice. Keep your bits sharp to avoid poor-quality edges and the risk of stress cracking.
IV. Secure the Acrylic Properly
Secure the acrylic meticulously to prevent excessive vibrations that could compromise the final product’s quality.
V. Implement the Ramp Feature
Use a ramping motion when moving the bit downward to avoid surface damage. Gradual ramping provides better protection and smoother finishing results. A smooth 1 to 3-inch ramp is ideal.
VI. Determine Pass Depth and Cutting Direction
For most materials, set the pass depth at half the bit diameter. Understand the CNC cutter’s rotation direction (left, right, clockwise, or counterclockwise) to achieve precise design features.
VII. Set the Correct Feed Rate
Adjust the feed rate appropriately to prevent acrylic melting. Faster feed rates are recommended but should be balanced to avoid excessive pressure or blemishes on the part surface. The best feed rate depends on the acrylic type and component geometry.
VIII. Optimize RPM
Correlate the RPM and feed rate to the acrylic type. Faster RPM requires a corresponding increase in feed rate to prevent material melting and achieve optimal results.
Proper Fixing of Acrylic Parts for Machining Operations
Ensuring secure workpiece fixation is crucial for achieving the desired quality in acrylic machining. Vibrations inherent in the process can disrupt the procedure if clamping isn’t adequate. The approach to securing the workpiece depends on factors like its size and the machining type required.
Although acrylic is sturdy, it remains a plastic material, necessitating a secure hold for larger sheets. Smaller acrylic parts can be clamped using jigs and vises, while longer or larger pieces often require methods like gluing or taping to the work table. For consistent precision and efficient machining of acrylic sheets, a vacuum hold table is a recommended choice.
Efficient clamping not only streamlines the work but also upholds the product’s quality.
Finishing Techniques for CNC Machined Acrylic Parts
Transparency, a key feature of acrylic, often obviates the need for surface finishes to maintain visibility. After achieving the desired precision and shape of acrylic components through CNC machining, post-processing techniques enhance their mechanical properties and functionality.
Polishing, the most common method, eradicates surface marks, imparting a radiant finish.
Texture finishing, widely employed, employs sand spray to create diverse surface textures.

Texture Acrylic (Reference)
Flame polishing, while yielding a clear, glossy surface, may introduce material tension and potential cracking.
Benefits of CNC Machining for Acrylic
· Precision and accuracy are guaranteed by the tight tolerances of 0.001″ to 0.005″ that are possible with CNC machining. This degree of precision guarantees that the manufactured product faithfully represents the intended design.
· CNC machines reduce manufacturing costs since they use as few raw materials as possible. CNC machining is a frugal option because of its increased production and lower material waste.
· Large-scale manufacturing is possible with CNC technology since the fabrication process is automated. The G-codes derived from the design files direct the cutting tool and regulate the process. Reduced human involvement from automation means uninterrupted production, no more tired workers, and more time for other tasks.
· CNC machining ensures constant quality because it permits careful management of several cutting parameters. This adaptability is ideal for producing acrylic components in a wide range of sizes and shapes. The outcome is superior to conventional machining in that it produces error-free acrylic parts.
· Acrylic’s thermoplasticity makes it simple to mold into different forms when heated, giving producers a chance to try out different mold designs at little cost and thereby cutting down on production costs in the long run.
· Transportation and setup expenses are reduced since acrylic is 50% lighter than glass of the same size. In addition, the cost of acrylic, whether in extruded, formed, or cast form, is often lower than that of glass.
· The impact resistance of acrylic is more than ten times that of glass, attesting to the material’s exceptional strength. Acrylic is appropriate for use in safety-critical items like shower doors and plexiglass windows due to its tendency to shatter into big, blunt-edged fragments upon impact.
· Acrylic’s durability and versatility in a variety of climates make it a great choice for outdoor usage. Cleaning acrylic is simple; just use a damp microfiber cloth and stay away from abrasive objects and ammonia-based cleaners to keep it looking sleek and new.
Applications of CNC Acrylic Parts
CNC PMMA parts find diverse applications in various industries, thanks to their unique properties. Their exceptional transparency and optical characteristics make them a popular choice in the lighting and electronics sector. CNC acrylic parts are ideal for crafting lamps, light tubes, and various light-emitting products, owing to their high light transmission and optical clarity.
In the automotive industry, CNC PMMA parts are used for car windows, panels, fenders, and motorcycle windshields. They are also employed for interior car light covers and indicator lights, thanks to their ease of fabrication and surface durability.

light cover (Reference)
The construction and architecture field benefits from acrylic’s high impact resistance and UV light resistance. PMMA parts are utilized in building doors, canopies, panels, window profiles, and façade designs.
In the healthcare and medical industry, CNC acrylic parts are employed in the production of cabinets, incubators, and glove boxes, owing to their ease of maintenance. Moreover, their compatibility with biologics makes them an ideal choice for dental cavity fillings.
Conclusion
To sum up, the remarkable adaptability and safety of CNC acrylic machining make it stand out in a variety of applications. PMMA processing is made efficient by CNC systems because of their ease of manufacture. This guide has provided insightful advice for the best outcomes while illuminating the advantages and machining procedures. Unleash your creativity by exploring the countless possibilities that come with painting with acrylic.


