The definition of reverse engineering
The term "reverse engineering," often referred to as "backwards engineering" refers to an approach in which one uses deduction and analysis to figure out how a complex machine or program works when only a limited amount of information is available. It's the method of breaking down a system to its component parts in order to improve or replicate it. The information obtained via reverse engineering may be put to use in a variety of contexts, including reusing old parts, performing a security audit, or just understanding how something works.
Reverse engineering frequently entails dismantling smaller parts of larger items. You can replicate a part by using the reverse engineering approach to learn how it was created. When buying a replacement item from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is not an option, businesses frequently employ this strategy.
As its name implies, reverse engineering includes going backwards through the initial design phase. You frequently know little about the engineering processes used to develop the product, though.

Process of reverse engineering
In order to reverse engineer a physical product, a manufacturer often buys a sample of the object under consideration and disassembles it to look at its inner workings. Engineers can then reveal details regarding the product's initial conception and construction.
Whether it's an aircraft, ship, vehicle, computer, or piece of industrial machinery, the first step in reverse engineering a mechanical product is to examine its dimensions and characteristics. You take measurements of the widths, lengths, and heights of the important product components during this study because these dimensions frequently connect to the performance capacity of the product.
Today, some engineers perform these kinds of assessments using 3D scanning technology. Engineers can accurately read the product's specifications using three-dimensional scanners, and their databases will automatically record this data. Coordinate measuring machines (CMM), industrial computed tomography (CT) scanners, laser scanners, and structured light digitizers are examples of 3D scanning technology.
You can utilize this information to build computer-aided design (CAD) drawings for further analysis and development after all the necessary information has been acquired and recorded. A product's design can be examined using CAD drawings, which are computerized two- and three-dimensional representations of the object. These digital representations assist in revealing design intent and provide guidance for developing a reverse-engineered component.
Due to the depreciation of parts from earlier years, reverse engineering is frequently required in the creation of computer components. For instance, you might have a product from two years ago with a special invention, but the manufacturer has now gone out of business. The engineering team will need to look at the technology of the outdated product in order to connect that innovation to a newer product for convenience and continuity's sake.
Purpose of reverse engineering
Manufacturers can learn about the design of a product or component through reverse engineering. Reverse engineering is the process of creating a virtual replica of the original design's blueprint.
Reverse engineering is arguably the most precise method for recreating designs for products that were taken off the market decades ago. Reverse engineering may be the only method for bringing such goods back to life in circumstances when the original blueprints have been lost or destroyed for a very long time. If you can find a working example of an outdated product, you can usually follow the design process' steps and apply what you learn to create a new model, fix a component, or create a better product in the future.

1. Replacement of legacy parts
Legacy components replacement, which entails studying and duplicating certain pieces of bigger machines to keep them functional, is one of the most popular reverse engineering applications.
A factory might, for instance, have a sizable engine compartment that powers the entire conveyor system throughout each workday's shift. One of the machine's components can occasionally wear out and require replacement. Because the OEM no longer manufactures the part or has gone out of business, certain parts may no longer be available if the machine is old.
The manufacturer could invest much on a new conveyor system, but keeping the existing machinery and replacing the problematic component is a better option. Reverse engineering allows you to digitally recreate the damaged part's design using a 3D scanner. The component can then be recreated and put into the machine as a new copy.
Reverse engineering a component could initially cost more than buying a newer or different model, depending on the size and complexity of the component in question. However, once you have successfully duplicated the item using a digital copy of the original design, you can continue to do so indefinitely by using that knowledge.
2. Service or Repair of Spare Parts
Understanding the operation of the product is helpful if maintenance or repair is required for a legacy part or a component the OEM no longer supports. This information can be used to correctly and quickly conduct the repair. Reverse engineering can be used by a corporation to produce design documentation if none already exist. Then, you can apply this knowledge to guide how you service or repair the component. Reverse engineering data can be used to identify which parts need to be replaced in order to solve a certain issue. By assisting you in comprehending the finest way to reach, remove, and replace a specific part, it can also guide your repair procedure.
3. Analysis of Failure
Techniques used in reverse engineering can be quite helpful for analyzing failures. You might need to disassemble a machine or look through the design files to figure out why it malfunctioned. Once you have this knowledge, you are able to repair or enhance the product so that it once again operates as intended.
Reverse engineering can be used to inspect a product and uncover broken components or flawed designs. Reverse engineering faults can also be discovered by looking at digital design files, which can assist you decide how to fix a piece of equipment.
4. Improvement of Parts
The development of parts also uses reverse engineering. After performing a failure analysis, a component might need to be changed, or a specific one might just require an upgrade. You might have the part reverse engineered to generate a replica of the original design if there isn't a replacement or other part available on the market. The design could then be altered to function better from there.
The defective portions will be measured, redesigned with higher thickness or stronger metals if a machine needs stronger joints or weld reinforcements. You can figure out which dimensions must be preserved and which elements can be changed by using reverse engineering.
5. Identification and resolution of issues
In a series of industrial operations, reverse engineering can also be utilized for diagnostics and problem-solving. A malfunctioning or underperforming function may occasionally cause the flow of operations in a factory to slow down. Finding the root of the issue can be challenging in production systems with various equipment and parts. By using reverse engineering, you may figure out how everything interacts with one another and utilize that information to pinpoint areas where problems can and do arise.

Several industries that utilizes reverse engineering
Automobile sector
Reverse engineering is used in the automotive industry for
- Studying and analyzing rivals
- Digitizing components from earlier car models
- Identifying flaws with current vehicles
- Creating replacement parts
Aerospace sector
This method is employed in the aerospace sector for
- Constructing airplane maintenance components
- Improving and repairing aircraft parts
- Performing an analysis of aerodynamics
- The production of tools
Consumer products sector
This method is employed in the consumer products sector for
- Creating prototypes for products
- Testing competitor's products for analysis
- Approval of conceptual designs
- Recording various design iterations
Examples of reverse engineering
· Modernizing and utilizing outdated machines/parts
Reverse engineering is a common practice among businesses when working with obsolete electronic parts like connection cards and printed circuit boards (PCBs). The products in concern frequently originate from companies that are no longer in operation. Even though the manufacturer is still in operation, the part might no longer be available. For the sake of continuity, the companies frequently reverse engineer outdated electronics.
Reverse engineering enables manufacturers to find these formulas and modernize an outdated piece of computer hardware if it has features that were later lost due to subsequent technological advancements. You can create components that connect the new and the old through reverse engineering, enabling users of older technology to connect their gadgets to cutting-edge computing hardware.
In some situations, reverse engineering is the only option to get the original product's design. The original 2D designs for certain older goods that haven't been manufactured in 20 years or more are no longer accessible. Since the original manufacturer may no longer be in operation, there is frequently no way to get in touch with them.
· Design Recovery
Reverse engineering is occasionally used by businesses to recover design information for long-gone products. For instance, a small business that has been operating for over 40 years might have produced a wide range of goods before the advent of computer-aided design and digital information storage. Therefore, it's possible that these earlier products were created using lost paper blueprints. Reverse engineering enables businesses to recover their lost designs and build archives of their past product lines.
Even if the business still uses paper blueprints, they could want to convert them to digital format so that they are more accessible and usable. This digital design file could be created by the company using specific reverse engineering procedures.
· Auto Restoration
Reverse engineering is occasionally used by experts in auto restoration to reproduce the designs of engines and auto body parts for older automobiles. Reverse engineering can be used to manufacture difficult-to-find parts or rebuild engines in order to restore drivability to 1920s–1950s automobiles. Reverse engineering has made it possible to entirely functionally restore old cars without altering their original system designs.
To precisely determine a product's dimensions, reverse engineering calls for a number of processes. Once gathered, the data can be kept in digital archives. Engineers frequently add fresh advances and changes to the design to improve it. On occasion, they will perfectly reproduce the original model.
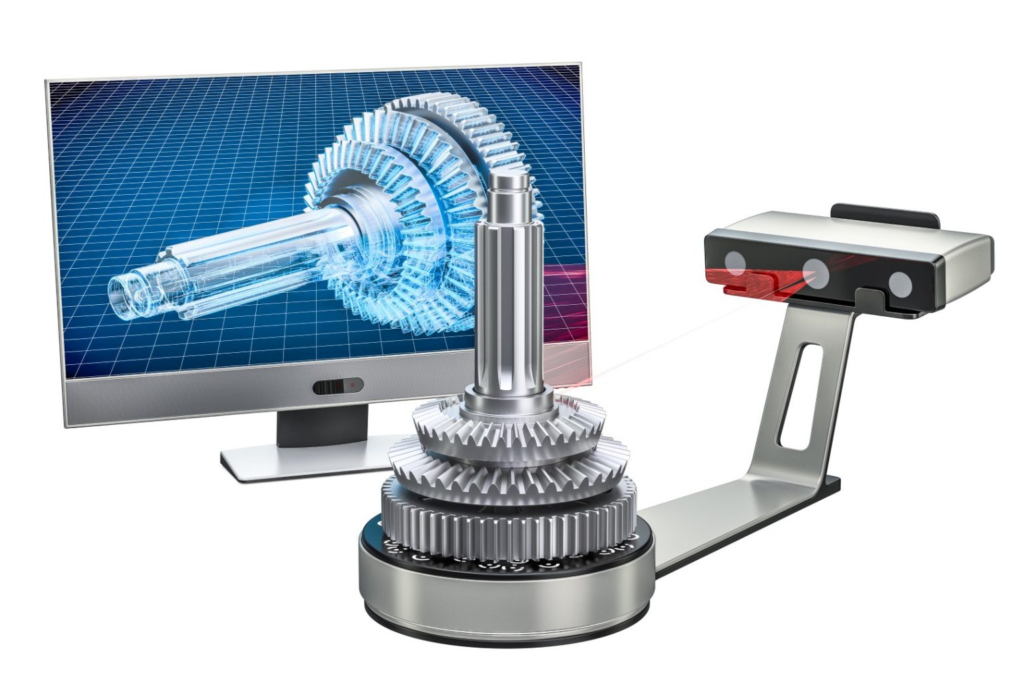

Challenges of reverse engineering
The transformation of a component's scanned data into meaningful information is one of the primary issues in RE. As was previously discussed in this article, this is accomplished by using CAD systems, which requires the processing of billions of coordinates of data and the conversion of that data into 2D drawings or 3D models. It's crucial and difficult to do this stage as quickly as possible, but if done effectively, it can significantly reduce the amount of time and work designers must put into their RE tasks.
Recovery of the geometry of damaged components whose geometry has changed significantly as a result of the difficulties of long-term operations, where the form could not be immediately recovered by conventional techniques like direct measurements or laser scanning, is another issue faced by RE. Designers only have the undamaged piece of the original part in this situation, which means that relying on the original may not be feasible to retrieve the desired portion due to a serious amount of damage.
Is reverse engineering the best solution for your project?
When acquiring the project requirements, reverse engineering is a helpful tool. Although it shouldn't be your primary method, it will give you some insightful information in the beginning of your project.
When used in conjunction with other early procedures, including document analysis, it will enable you to formulate more effective questions for your stakeholders.
Reverse engineering is particularly useful in the following situations:
- when the present product comes with little or no documentation
- When an outdated product or system is being used
- when vital information has been lost and records weren't maintained
- when the present system or product evolved naturally without a clear design plan
These ideas are significant when anything is being improved upon that is already in existence.
However, it is also possible to reverse engineer foreign items. To gain a better idea of what needs to be accomplished, you might immediately refer to it if the customer wants to copy a competitor's product.
Advantages of reverse engineering
Engineering is a creative and adaptable field. Modern engineers create innovative goods that help their clients using both innovation and creativity. These engineering items are essential for fostering local economic growth and facilitating corporate interactions. But one thought occurs to you when you consider innovation. How do engineers of today stay creative in today's hectic commercial world?
Reverse engineering is how the answer is discovered. Reverse engineering plays a significant role in innovation and sparking ideas that address demands across a variety of business industries. Fundamentally, reverse engineering involves taking apart broken objects to examine each component's performance before incorporating the results into new products.
· Examine existing plans and strategies
Investigating an existing thing is possible through reverse engineering. This could be a feature, procedure, or framework that aids a particular community. By analyzing currently on the market products, reverse engineering will assist engineers in discovering and innovating.
· Make an updated version of an outdated product
It is crucial to make an effort to know how a current product functions in order to revamp it. Since reverse engineering offers the chance to work on outdated quirks in an older system, engineers will be able to smoothly reconstruct outdated components while maintaining quality. There won't be any quality flaws, thanks to reverse engineering.
· Recognize product shortcomings
Reverse engineering can be used to identify a product's shortcomings. This helps to guarantee the safety and welfare of the customers. Reverse engineering enables the detection of all such issues during the research process itself, as opposed to learning about them following the distribution phase.
· Bring more affordable and effective products to market
The basic goal of reverse engineering is to direct engineers toward success and innovation. Engineers can use reverse engineering as a strategy to save production costs while maximizing a product's efficacy.
· Producing a CAD model for later usage
Reverse engineering activities require a fully working CAD file, which is normally saved for later use. A CAD file is often created in order to digitally analyse engineering elements in case of future issues. This reverse engineering strategy has improved engineering productivity as well as product expressiveness.
· Reverse engineering offers a route for creative design
Reverse engineering makes way for innovative design at the end. A method used in engineering to help uncover systems that can be useful for unrelated projects is called reverse engineering. By applying reverse engineering, engineers can relate tasks to their existing knowledge and come up with new ideas.

Summary
Reverse engineering is essential for the continuity of the current industrial systems as technology develops and advances. Without reverse engineering, businesses would be needed to replace entire devices frequently, incurring significant financial costs.
No matter how old the product is or if the original manufacturer is still in business, reverse engineering allows you to keep the pieces that function and replicate the ones that don't.
Although it is lawful to reverse engineer as long as no one intentionally copies another product, the ethical discussion will undoubtedly continue. There are numerous appropriate applications for reverse engineering. Recreating historic pieces, improving an existing product, or making it more affordable can be both a legal and ethical course of action. Depending on what is being reverse-engineered, there are numerous difficult steps. Although it can be challenging, reverse engineering greatly reduce the amount of guesswork.