In the manufacturing process of CNC machining, numerous tools are used. These tools are one of a kind, yet they also come in a wide variety. As a result, each one can be used for a variety of purposes. When it comes to CNC machining, the terms "jig" and "fixture" are often used interchangeably.
This article will explain the differences between jigs and fixtures in regards of their categories, variations, and applications in order to clear up the misconception. Is it possible to answer this question, "What are Jigs and Fixtures for?" at the end of this course? Are you ready to learn everything there is to know? Time to get started!
What is a Jig?
To keep the cutting tool steady while a precise operation is being performed on the workpiece, this device might be used. A common jig component is a hardened steel bushing that serves as a guide for other cutting instruments. If you're working with another person, you'll need a jig to help guide them. A jig can provide you with accuracy, interchangeability, and repeatability in the production phase. In this case, the tool is directed by a mechanism that retains the work, which is called a "jig." Many times, copying keys involves using the original as a guide to guarantee that they are re-created exactly as they were before.
Jig Uses or Applications
Jigs are frequently used in one-dimensional machinings, such as drilling, reaming, counter boring, tapping, and another one-dimensional machining, or as guidelines for tools in other businesses, such as furniture, where particular cramping jigs maintain square shape. Another typical use for a jig is to direct a power drill through the surfaces of a machining object. It will make sure it is positioned and angled correctly.
What are the Types of Jigs?
In CNC machining, jigs are standard tools that come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Jigs often used in milling processes are listed below.
1. Template Jigs

These template jigs are basic, yet they are great because of their precision. They're also really fast. Machinists, on the other hand, prefer to use them for their accuracy over their speed. Template jigs can be put to a variety of uses. This means that they can be used in a variety of ways. Clamps, on the other hand, are rarely used.
2. Angle-Plate Jigs

Using angle-plate jigs, you can hold drilling-ready items at an angle to their mount locators.
3. Plate Jigs

A plate jig is a type of template jig, and it is used in the same way. There are some advantages to using these jigs over template jigs.
4. Leaf Jigs

Part loading and unloading are made easier by the use of a hinged leaf on the jigs. There is a gap in the hinged leaf's coverage of the component.
What Is a Fixture?
It is a work-holding device; it not only holds and maintains the component but also places it for a specific operation, all without using cutting machine through it. It can only be used with a base point or a gadget. Fixtures are one-of-a-kind since each one is made specifically to fit a specific portion or shape. A fixture's principal role is to locate and, in certain cases, grab the workpiece when it is to be milled or otherwise processed. There are two distinct differences between workpieces and fixtures: The workpiece is located and supported, whereas the tool is positioned in a specific way.
What are the Types of Fixtures?
Fixture classification is a term that is unfamiliar to the majority of machinists. It's no wonder they're having a hard time deciding which one is best for their business. Machining procedures, intended uses, and power sources all go into the design of the fixtures.
Distinguishing Between Types of Fixture Tools
Modular Fixtures

Universal Fixtures

Combination Fixtures

Assembled Fixtures

Special Fixtures

Based on the Power Source of the Fixture Tools
Magnetic fixture

Manual fixture

Electric fixture

Pneumatic fixture

Vacuum fixture

Hydraulic fixture

What are the Major Differences between a Jig and Fixture?
People who are new to CNC milling in general or to fastening the object on CNC machining may find the jig and fixture intimidating. Productivity and time efficiency can be achieved with the use of both tools. They do, however, perform in distinct ways. Some of the most significant distinctions between jigs and fixtures are outlined below.
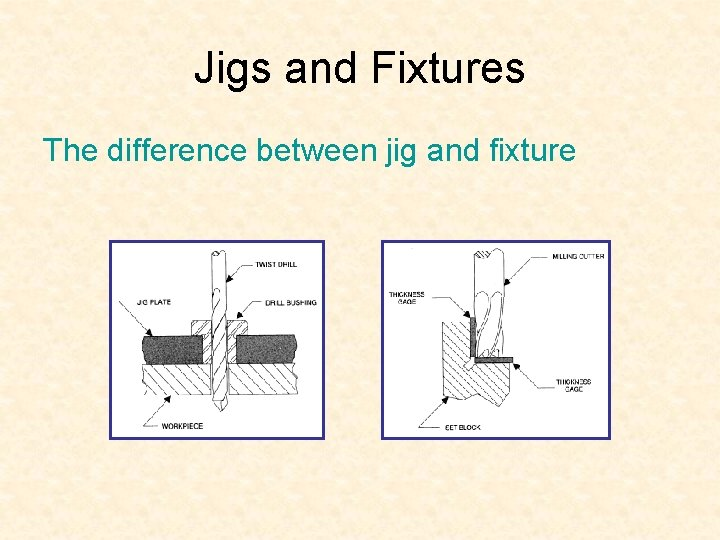
1. Core Function
The most significant differences between jigs and fixtures are in their primary purposes. Workpieces are placed in a jig, which directs the cutter to a specific location on the surface. The part is likewise supported and located by this. Workpiece security, support, and location are the only functions of the fixture. The machine portion is not guided by this component.
2. Complexity in Type
Machine operators often feel that jigs are simpler to use than fixtures. Before executing an operation on a fixture, machinists will need to have a specific set of skills.
3. The Weight
The fact that jigs are less heavy than fixtures is a further consideration. Because of the high cutting force and vibration, the fixtures are heavier.
4. Ties to the Machine
When working with jigs, they can either be held or secured to the table, depending on the task at hand. Although they may need to be clamped, jigs do not necessitate additional equipment when working with heavy materials. Clamping and other accessories are necessary for fixtures to function properly.
5. The Design
In terms of construction, jigs are more difficult to master than fittings.
6. Connection with the Tool
Due to their design, fixtures don't need to come into direct contact with a machine part. To correctly set the angle and location, a jig must come into contact with the tool. The following table briefly cites the differences between a jig and a fixture.
| Jig | Fixture |
| The machining tool is controlled and guided by a jig | For machining processes, a fixture secures and stabilizes the part in place |
| The use of a jig helps to assure precision, consistency, and interchangeability | To reduce the risk of human mistake, the fixture secures the component to the tabletop |
| Jigs tend to be more upbeat and carefree | It is big, clunky, and hefty |
| Hand pressure can be used to secure jigs in place | Fixtures are constantly affixed to the machine table |
| There are several standard jig functions: drilling, reaming, tapping, bore | In milling machines, slotting machines, and shapers, the usage of fixtures is particularly prevalent |
| Jigs charge more | In comparison to Jigs, fixtures are more expensive |
| A jig requires a wide range of complex design procedures | The process of creating a fixture is much simpler |
What are the Benefits of Jigs and Fixtures?
The usage of Jigs and Fixtures has improved production efficiency, precision, and ease of use. The following are just a few benefits of using jigs and fixtures:
- Increased output and consistent product quality owing to minimal dimension variability
- Reduced expenses for examination and quality control due to interchangeable parts and high precision.
- A decrease in the number of accidents as a result of better safety regulations
- Slightly skilled individuals can operate these instruments due to their ease of movement, which lowers the overall cost of staffing a facility.
- To a fair extent, the machines can be automated
- Assemblies that need only basic hand tools can save time by eliminating the need for many steps such as measuring, punching, and trying to set up for each piece of work to be assembled.
- Enhances machine tool technological capabilities
- Because of the improved clamping capabilities of jigs and fixtures, it is possible to set greater values for some operational circumstances such as cutting depth, speed, and feed rate.
How Do You Make a Jig and Fixture?
Location Points: The work should be located in a convenient location with enough facilities. To avoid wasting time repositioning the workpiece, the jig must be simple to use and quick to remove the workpiece from the jig. Tool guidance in the jig or fixture setting parts requires that the workpiece be precisely positioned.
Foolproof: Foolproof jigs and fixtures prevent the workpiece or tool from being put in any other position than the one intended.
Reduction of Idle Time: It is important to design Jigs and Fixtures in a way that minimizes the time it takes to load, clamp, and unload the workpiece.
The Weight of Jigs and Fixtures: If it's small, lightweight, and inexpensive to make, it should be strong and sturdy without losing ease of use or portability.
Jigs Provided with Feet: It is common for jigs to be equipped with feet to allow them to be positioned on a machine's worktable.
The Materials: Most commonly, they are built of toughened materials to withstand wear and tear. MS, Cast iron, Diesteel, CS, and HSS are some examples.
Clamping Device: As simple as feasible while still being effective is the goal of the clamping device when building jigs and fixtures, the clamp's strength is such that it not only securely holds the workpiece but should also be able to withstand the force of the milling cutter without breaking.
What are the General Rules for Designing?
- It's easy to see that building costs don't outweigh predicted gains when you compare the current costs of manufacturing with those of the tool that's being created.
- Decide on where the clamping points will be and draw a diagram of the configuration.
- As much as possible, make clamping and binding tools as quick-moving as possible.
- Ensure that the jig is impenetrable.
- Adaptable locating points should be included. Make some of them.
- Simple clamping arrangements are preferable to more complex ones.
- Handles should be provided in places where they will make it easier for people to lift and carry.
- Make a lot of space available.
- Make holes in the escapes for the chips you'll be using.
- Make sure the clamps are placed in the best possible position to withstand the cutting tool's pressure.
- To avoid springing, position all clamps as close as possible to the work's bearing point.
- All jigs should be tested as soon as possible before being used in the shop.
What Type Materials are used to Make Jig and Fixture?
For example, toughened jigs and fixtures are composed of a range of different materials.
Materials Used:
- Cutting tools such as drills, screwdrivers, and milling cutters are made of high-speed steel.
- 0.5-1 percent tungsten and less silicon and manganese are found in die steels, which are used in press tools.
- Cutting tools are made of carbon steel.
- One percent carbon, one percent manganese, and less than one percent silicon are called "collet" spring steels.
How to Combine the Jigs and Fixtures to Enhance Precision?
The manufacturing precision needed to make things that work properly is made possible through the use of jigs and fixtures. Take a look at the doors, cabinets, and storage in your home. Doorknob, latch, and hinge holes must be drilled in precise locations or with the help of a guide. It's like cabinets that have dovetail cuts or side shelves. For example, books would fall off the shelf without jigs and fixtures, drawers and doors would be fragile, and they wouldn't close properly.
Better Output and Efficiency: Machine idle time is decreased since the two tools reduce alignment, and increase efficiency and productivity.
Reductions in Manufacturing Cost: By utilizing them, product manufacturing costs can be reduced while quality and productivity can be improved. You may read about CNC machining costs in an article we've published.
Enhancement in Quality of Product: Machine operators no longer have to manually separate parts during their work. As a result, human error is reduced, and higher quality is achieved.
Easy-to-Manufacture Intricate and Heavy Tools: Machinists can readily produce heavy and complex-shaped items using these tools. This is because the workpiece is held in place by the two tools during the machining process.
Increases Safety: It's safer because the jigs and fixtures are connected directly to the piece and machine, removing the need for human intervention.
What is the Application of jig and fixture?
The following are the applications of jig and fixtures –
1. Jig Can Enhance the Manual Intervention
Engineers use the term "jig" in a different context from the one you might be familiar with from your weekend fishing adventures. Jigs are used to hold tools in place while we carry out a manufacturing activity. It's usually a one-of-a-kind piece that assures that holes are drilled and tapped accurately and consistently.
Jigs frequently use drill bushings. Using them ensures that a drill's location and angle are always precise. Drill bushings not only improve the quality of the work, but can also speed up production.
2. Fixtures Could Automate the Manufacturing Process
An essential part of automation is the use of manufacturing fixtures. Fixtures are a necessary part of almost every industrial process that is automated. Fasteners that secure and guide automobiles through the soldering and assembly process, for example, are essential to the operation of an automobile assembly line. When utilized in conjunction with optical and laser scanning, they can also be employed for product holding during quality assurance inspections of the manufacturing process. Fixtures abound in any factory tour.
Bottom Line
When it comes to making jigs and fixtures, the most frequent manufacturing procedure is CNC machining. When machining the geometry would be too complex or expensive, the best option may be to use 3D printing. Consider not all fixtures and jigs have to be constructed of metal. Using plastic in many applications can save you money and meet your design requirements.
Rapid manufacturing won't replace your existing machine shops, but it can be a useful tool for generating templates for jigs and fixtures, as well as less important parts that don't require extreme precision.





