With the advent of modern technology, mostly electric and mechanical components are becoming compact, powerful, and advanced. These devices often get heated during working due to excessive load and compact machinery, for that reason designing appropriate heat sink mechanisms is becoming more challenging day by day. Scientists are working on different materials and designs to meet up this modern-day requirement. This article covers thoroughly why heat sinks are important and how they are made in the industry.
What is a Heat Sink?
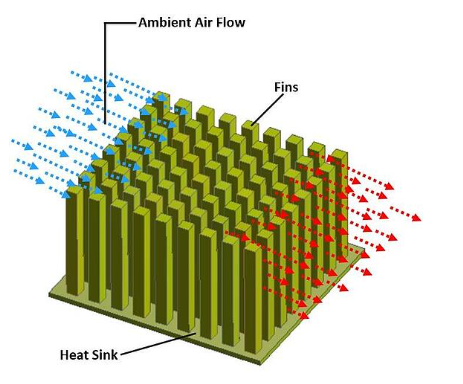
Heat sinks are actually electronic devices, which are used in electrical or mechanical machines to remove unappropriated heat generated. These devices are made of those materials which have good thermal conductivity, aluminum, copper, etc. The heat generated in the components is absorbed by the fluid present in the heat sinks and thrown away to the external environment. The fluid is usually air or some thermal conductive fluid present in its fins.
The working principle of heat sinks depends upon the Fourier law of heat transfer, and the mechanism is to transfer heat from higher-temperature reservoirs to low-temperature reservoirs, which are compact machinery to air in this case. Heat sinks are mostly used in electronic systems, CPUs, GPUs, supercomputers, lasers, electronic units, power transistors, and in much more niches.

What are the types of heat sinks?
Heat sinks are designed as per the application requirements because if the temperature of the system exceeds the operating conditions, the system may get damaged or it may lead to part malfunctioning. A well-researched and proper calculation is required before designing any heat sink. Heat sinks are of various types, they are mostly categorized on the working mechanism and fins placements.
Passive heat sinks:
Passive heat sinks are those which rely on natural air convection, they don't need any external source for heat removal. The working principle of these sinks depends upon the buoyancy of hot air, which causes the airflow between fins, these heat sinks are used where we have to deal with less heat removal and the optimal temperature of the working system is high.
Active heat sinks:
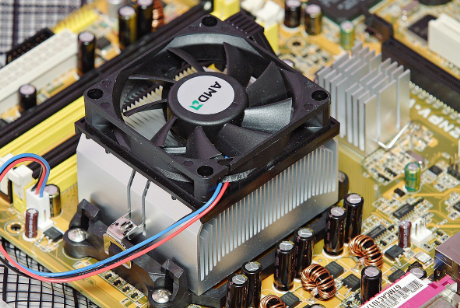
Active heat sinks need a suitable source or control unit, they are also known as unidirectional heat sinks. An external source like a fan or blower is needed for the airflow between fins. They are mostly used where we have to deal with high temperatures. For example, Motorbike engine fins are designed such that they perform cooling operations through fast-moving air.
Hybrid Heat Sinks:
Hybrid heat sinks are rarely used, but they are the most advance and effective in heat removal. The working principle of these sinks is active as well as passive when the system's temperature is low, these heat sinks do natural convection, while when we are dealing with high temperature the control start forced convection, by turning on the system fan. The best example of these types of heat sinks is Super-computers, which are highly sensitive and need these types of mechanisms for cooling.
How Heat Sinks Are Made?
Heat sinks are designed as per the application requirements, thermal conductivity, thermal sensitivity, and heat flow intensity are some of the important points that should be kept in mind while making a heat sink. After the material, the design of the find, their distance, and airflow ratio are the parameters that define the overall geometry.
Different industries use different methods to prepare these heat sinks but the most famous ones are discussed under.
Extrusion:
It is the most common industrial process for making heat sinks, in this process, hot metal billets are passed through the dyes to obtain the required shapes.
Mostly soft metals like aluminum 1050 are treated through this process, it is the fast, most economical, and most effective method of making heat sinks on an industrial scale.
CNC Machining:
CNC machining is another effective way of making heat fins. The mechanism involves cutting fins through a bulk portion of huge metal parts. CNC machining is famous as one can achieve highly complex structures and designs through this process. This technique is useful whether you are dealing with soft metal or hard metal.
Skiving:
Skirving is a technique in which metals are cut in slices to obtain the desired shapes, it is used for the manufacturing of thin fins. The heat sinks made from this process show good performances in electrical devices, especially in chipboards.
The fins produce are thinner as compared to extrusion and they are tightly packed, so they are able to show a good airflow ratio between fins, which removes the excessive heat quickly.

Casting:
Casting is another way of making heatsinks, in this process, molten metals are poured into the required shaped dyes, and the metals take the shape of the dyes. Casting is also a very economical and effective manufacturing process. Through casting, manufacturers are able to make complex structures with excellent mechanical properties. It is mostly used for manufacturing zinc heat sinks.
Appropriate Materials for Heat Sinks:
Choosing an appropriate material for heat sink manufacturing is the key step toward their efficiency. As described earlier the overall properties of the heat sink depend upon the conditions of the system. However, the following are the key points of an ideal material for manufacturing any heat sink.
- High thermal conductivity
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion
- Low density
- Low-cost

Aluminum:
Aluminum and its alloys are considered the best material for preparing heat sinks. This is due to the excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum which is approximately 229 watts per meter-kelvin (W/m•K). Moreover, aluminum is a soft metal and it shows low mechanical strength that's why it is easy to cast machine and extrude. Aluminum is mostly used for building microprocessor processor supercomputers control unit’s laser beams and other related domains. some of the famous aluminum alloys used for making heat sinks are

- Aluminum 1050 shows excellent thermal conductivity, It exhibits a thermal conductivity of 229 watts per meter-kelvin (W/m•K). It is mostly used in CPUs and GPUs.
- Aluminum alloys 6063 and 6061 are mostly used in the manufacturing of one-piece heat sinks. They show excellent thermal conductivity of201 and 166 W/m•K, respectively. They are mostly used in the automobile sector, in engine fins, and in heavy machinery heat-sinking mechanisms.
Copper:
The thermal conductivity of copper is (401 W/m•K) which is twice aluminum, and it shows high thermal resistance, biofuel resistance, and corrosion-resistant properties. However, copper is denser and more ductile than aluminum. Some manufacturers also used aluminum fins with copper base plates. This gives benefits to both materials and enhances the thermal properties of the heat sink.
Another material having ideal thermal conductivity (2200 W/m•K) is diamond, but it is way costly and used in highly integrated circuits, like supercomputers, or in aeronautical chips where necessary. few composite materials, such as copper-tungsten pseudo alloy and Dymalloy (diamond in copper-silver alloy matrix),) are also considered ideal materials for heat sinks.
Conclusion
Heat sinks are crucial parts of any electronic or mechanical device, so you can consider the best material, and type based on our requirements. Furthermore, design, manufacturing, cost-effectiveness, budget, heat dissipation level, and thermal conductivity are the factors that should be checked before considering any system. Secondly, you should choose the best machine shop for CNC machining and extrusion processes.





