How do airplanes endure the extreme strain of landing and taking off? What guarantees that their landing gear, an essential part, always operates perfectly? Advanced manufacturing processes and precision engineering hold the key to the remedy.
In the fast-paced aviation industry, landing gear systems must adhere to stringent reliability, durability, and efficiency standards. However, how can the industry handle the challenge of traditional production methods reaching their limits?
Here's where computer numerical control, or CNC, machining comes into play. Landing gear system design and manufacturing are being revolutionized by CNC's capacity to produce lightweight, high-strength components with unmatched precision and consistency.
Can this technology help the aviation industry satisfy its increasing cost-effectiveness, performance, and safety demands? Let's examine how landing gear systems for aircraft are evolving due to CNC machining. So, Let’s begin.
2. Components of Aircraft Landing Gear
Why can the landing gear of an airplane endure the tremendous forces involved in takeoff, landing, and taxiing? The solution is found in its complex design and the cooperation of several parts, each essential to maintaining performance and safety. To appreciate the engineering miracle that is modern landing gear, one must have a thorough understanding of these components.
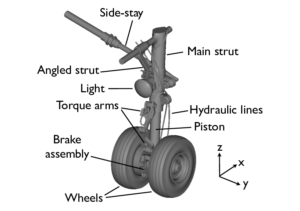
1. Struts
The landing gear system's main component, the struts, absorbs shock and loads produced during landing. They offer the required stability and structural support and are usually composed of high-strength materials like steel or titanium.
Function:
- Absorb forces during takeoffs and landings and support the aircraft's main weight.
- Permit the plane to stay stable when on the ground.
Design:
- Usually composed of titanium alloys or high-strength steel, these devices' stress-absorbing capabilities are accomplished via hydraulic or pneumatic shock absorbers.
2. Nose Landing Gear (Nose Gear)
The nose gear, which is situated at the front of the aircraft, supports the nose during landings and takeoffs and provides directional control while taxiing.
Function:
- Enables the aircraft to be guided on the ground, generally via a nose-wheel steering system.
- Sustains the forward section of the aircraft's weight.
Design:
- Comparable to the main gear, although usually lighter and smaller. It is made to withstand different stress loads than the main gear and frequently has its shock absorption system.
3. Tires and Wheels
Wheels and tires are essential for safe ground operations since they are made to withstand heavy loads and withstand wear. Aircraft tires are designed to withstand extremes in temperature and pressure.
Function:
- Assist the aircraft's full weight when it is landing and operating on the ground.
- For takeoff and landing, absorb runway shocks and keep a smooth contact.
Design:
- Tires are made of high-strength alloys and are intended to endure high pressures and speeds.
- Rubber compounds designed to offer durability, traction, and heat resistance are commonly used to make tires.
4. Braking Systems
When an airplane lands, how does it stop? The braking system, which includes electronic or hydraulic brakes and cutting-edge anti-skid technology, is in charge of stopping and keeping the aircraft under control on the runway.
Function:
- Offers braking for landing and taxiing.
- Collaborates with the aerodynamics and thrust reversers of the airplane to safely stop it.
Design:
- Brakes have a high degree of heat and wear resistance and are frequently disc-type or carbon-based. To preserve stability and control when braking, the anti-skid system makes sure the tires don't lock up.
5. Shock absorbers (pneumatic or hydraulic)
How does a plane take in the force of a landing? Shock absorbers disperse energy during landing to maintain structural integrity and passenger comfort. They frequently use compressed air and hydraulic fluid. Shock absorbers are essential to reduce the energy generated during landings and other ground operations. They lessen the forces that passengers and cargo must endure while also safeguarding the aircraft's structure.
Function:
- Prevent aircraft damage by absorbing and dispersing the energy produced during landing or taxiing.
- Reduce vibrations to guarantee smooth functioning.
Design:
- Usually, pneumatic (using air) or hydraulic (using fluid) systems are used to reduce forces. These are built into the struts and are frequently movable according to the weight of the aircraft and its operating environment.
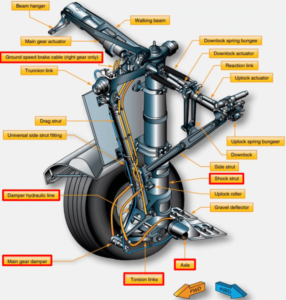
6. Steering Mechanism
The pilot or ground crew can control the aircraft during taxiing due to the steering mechanism in the landing gear, which enables ground maneuverability.
Function:
- Enables the aircraft to be guided on the ground by turning the nose gear, particularly when taxiing.
Design:
- Usually consists of a mix of mechanical links and hydraulic actuators. While some aircraft may employ a more complicated system with independent steering, others may have the nose wheel directly connected to the cockpit controls
7. Retraction Techniques
The landing gear can retract into the wings or fuselage while in flight thanks to the retraction system, which improves aerodynamics and lowers drag.
Function:
- During flight, the landing gear retracts and locks in position.
Guarantees a simplified and effective design while the equipment is not in operation.
Design:
- The retraction mechanism, which can be powered by electricity or hydraulics, is made to firmly lock the landing gear in both extended and retracted states.
8. Actuators and Connections
The mechanical systems that convey the forces required to extend, retract, and steer the landing gear are called links and actuators.
Function:
- Give the landing gear the force and motion it needs to extend or retract.
- Allow the plane to move during taking off or taxiing.
Design:
- Depending on the size and design of the aircraft, actuators might be hydraulic, electric, or mechanical.
- Joints and connections
These parts facilitate smooth functioning and evenly disperse loads. They link different landing gear components and are designed to withstand heavy weights and repeated stress.
The landing gear system's joints and connections help maintain both the structural soundness and smooth functioning of its many parts.
These components act as the connections between other components, allowing for alignment, weight transmission, and movement in dynamic circumstances.
Function:
- Load Distribution: To guarantee that the system can sustain the stresses of landing, taxiing, and takeoff, connections and joints distribute loads across parts including struts, wheels, and actuators.
- Articulation and Motion: Steering, shock absorption, retraction and extension of the landing gear are all made possible via hinged and rotating joints.
Design:
- Pivot joints provide for smooth rotation during extension and retraction and are found in retractable landing gear systems.
3. Why is CNC machining essential for Landing Gear Systems?
An aircraft's landing gear system is a vital safety component that needs to be incredibly strong, precise, and long-lasting. CNC machining is essential for these systems because of their rigorous operating circumstances, which include strict safety regulations, harsh environments, and heavy loads. The following justifies the importance of CNC machining in the production of landing gear systems:
1. Superior Accuracy and Precision
To guarantee smooth operation and safety, landing gear components need to adhere to incredibly strict tolerances. CNC machines' ability to attain micrometer-level precision is crucial for components like shock-absorbing devices, axles, connections, and hydraulics systems.
2. Consistency in Large-Scale Manufacturing
Consistent component quality across several units is necessary for aircraft manufacturing.
By creating similar parts with little variation, CNC machining guarantees regularity.
3. Capacity to Handle High Strength Materials
To bear heavy loads, landing gear components are composed of materials like titanium, high-strength steel, and aluminum alloys. These difficult materials may be handled effectively by CNC machining without sacrificing accuracy or quality.
4. Complex Geometries
It is challenging for conventional machining to accomplish the complex designs of landing gear mechanisms, such as retractable systems and shock-absorbing connections. These intricate forms are easily produced by CNC machines, especially those with 5-axis systems.
5. Enhanced Safety and Reliability
In aerospace applications, safety is crucial. Components that are CNC machined are guaranteed to satisfy strict industry certifications and requirements, including those established by the FAA and EASA. CNC machines with real-time quality control systems can identify and fix manufacturing problems.
6. Rapid Customization and Prototyping
Iterative testing and prototyping are frequently necessary for aircraft designs before final manufacturing. Prototypes can be produced quickly and easily using CNC machining to meet precise design specifications.
7. Support lightweight designs
Weight optimization is essential for aircraft performance. CNC machining makes it possible to produce lightweight components by carefully cutting away extra material without compromising structural integrity.
4. Materials Used in Landing Gear Systems
The selection of materials is essential for ensuring effectiveness, safety, and performance while producing aircraft landing gear. While maintaining the lowest feasible weight, landing gear components must be able to endure heavy loads, high stress, and adverse environmental conditions. Advanced materials and careful material selection procedures are used to attain this state of balance.
Strengthened Alloys
High-strength alloys, such as steel and titanium alloys, are frequently used in aircraft landing gear systems due to their remarkable qualities:
- Titanium Alloys: Crucial load-bearing components are best suited for titanium alloys, which are distinguished by their high strength-to-weight ratio, resistance to corrosion, and resilience to fatigue. They contribute to the overall weight reduction of the aircraft while preserving its structural soundness.
- Steel Alloys: For components like landing gear struts and actuators, steel alloys are essential due to their exceptional hardness, resistance to wear, and capacity to withstand tremendous stress.

2. Aluminum Alloys
In less crucial parts of the landing gear, where lightweight characteristics are more crucial than exceptional strength, aluminum alloys are employed. They are appropriate for auxiliary components due to their exceptional machinability and resistance to corrosion.
3. Composite Material
Composite materials are being used in landing gear designs due to recent developments. These materials—like carbon fiber-reinforced polymers—are being utilized more and more because of their remarkable strength and lightweight nature, which helps to further reduce weight.
Role of Material Selection in Weight Reduction and Load-Bearing
Landing gear system performance is directly impacted by material selection. The overall weight of the airplane is decreased by lightweight materials like titanium and composites, improving cargo capacity and fuel efficiency. High-strength alloys guarantee the landing gear's capacity to sustain the tremendous weight encountered during takeoff, landing, and taxiing, as well as safety and dependability.
Challenges in Aerospace-Grade Material Machining
Despite their exceptional performance, these materials provide considerable manufacturing challenges:
- Machining difficulty: The hardness and toughness of high-strength alloys and composites make them difficult to manufacture, necessitating the use of sophisticated methods and equipment.
- Tool Wear and Heat Generation: Working with materials of aerospace quality frequently results in excessive heat and quick tool wear, which calls for specialized cooling and careful control.
- Strict Tolerances: Due to the vital function of landing gear systems, exact machining tolerances must be strictly adhered to, leaving no margin for error.
5. CNC Machining Processes Involved in Landing Gear Production
The process of creating landing gear systems is extremely intricate and requires precision. Manufacturing processes for these vital parts must be able to manage complex designs, high-strength materials, and strict tolerances. The following are the main machining procedures used in the manufacture of landing gears:
1. CNC Milling
A key component of landing gear manufacturing is CNC milling. Using it, intricate geometries like wheel hubs, actuators, and struts may be precisely created. High-speed milling machines are frequently used to work on materials of aeronautical quality, such as steel alloys and titanium.

2. CNC Turning
CNC turning is used to create cylindrical parts like linkages, pistons, and shock absorbers. While the workpiece is being shaped to the required dimensions by cutting tools, it is rotated. This technique guarantees precise measurements and smooth surfaces.
3. The Grinding
Tight tolerances and clean surface finishes require grinding, particularly on crucial parts like bearings and hydraulic pistons. The ability of parts to endure severe stress and perform dependably in harsh environments is guaranteed by precision grinding.
4. Boring and Drilling
Accurate holes for fasteners, hydraulic lines, and other attachments are made using drilling and boring techniques. Modern CNC drilling equipment guarantees precision and consistency, which are essential for components that support weight.
5. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
For machining complex features and hard materials that are challenging to accomplish with traditional techniques, EDM is especially helpful. Sharp edges and fine details are frequently created with it in high-strength metal components.

6. Surface Finishing
Surface finishing occurs to improve durability corrosion and wear resistance after the basic machining procedures. Methods including anodizing, shot peening, and polishing are used to increase longevity and performance.
7. Roll Forming
To create curved profiles or reinforced edges for auxiliary landing gear components, roll forming is utilized to shape sheet metal or tubular materials. It provides a constant process and guarantees consistency for mass manufacturing. Its material efficiency compared to alternative shaping techniques, material efficiency reduces waste.
8. Forging
Axles and struts can be pre-shaped using forging, which lessens the amount of material that must be removed during later machining operations.
- Near-Net Shaping: Reduces waste and time spent on machining.
- Improved Material Properties: The strength and fatigue resistance of forged parts are superior.
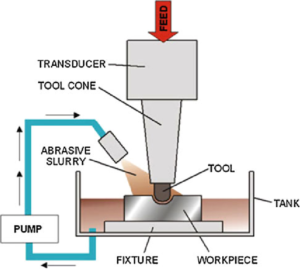
9. Ultrasonic Machining
High-frequency vibrations and abrasives are used in ultrasonic machining to remove material. It works especially well for complicated or delicate elements in composites or fragile materials.
- Non-Thermal Process: High-performance alloys are protected from heat damage.
- Micro-Machining Capability: Beneficial for tiny, intricate parts such as mounting plates or sensor housings.
10. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing is rapidly being utilized to create lightweight components or molds for landing gear elements, while it is still mostly used for prototyping.
- Metal Additive Manufacturing: Complex, lightweight structures that are challenging to process conventionally are produced.
- Hybrid machining: For ultimate accuracy and finishing, 3D-printed parts are combined with CNC machining.
11. Surface Treatment for the Landing Gear System
To improve the longevity and fatigue resistance of landing gear components, surface treatments such as shot peening, polishing, and coating are essential. Polishing minimizes wear by reducing surface roughness, whereas shot peening adds compressive stresses to increase fatigue life. Reliability in harsh operating conditions is ensured by coatings that prevent corrosion and wear, such as anodizing, thermal sprays, and hard chrome plating.
6. Key Challenges in Landing Gear Machining
Several difficulties arise while machining landing gear components because of the rigorous specifications of aerospace manufacturing:
- Material Toughness: Cutting alloys of high strength, such as steel and titanium, is challenging and necessitates sophisticated cutting methods.
- Precision Requirements: Extensive quality control and sophisticated CNC machines are required due to extremely tight tolerances and complex geometries.
- Thermal Management: Because heat produced during machining can cause material distortion and decreased component integrity, efficient cooling techniques are required.
- Surface Finish Standards: It can be difficult, particularly on hard materials, to achieve perfect surface finishes for fatigue resistance and operating efficiency.
- Time and Cost Effectiveness: A persistent difficulty is managing production schedules and budgets with the high cost of materials and machining procedures.
7. Role of CNC Technology in Precision Machining
For landing gear systems to be manufactured with the level of precision needed, CNC technology is essential. CNC machines provide remarkable precision, reliability, and efficiency by automating and streamlining machining operations.
- Unmatched Accuracy: For landing gear parts like struts, actuators, and pistons, multi-axis CNC machines provide precise tolerances and complex geometries.
- Consistency: An essential feature for aerospace applications, CNC technology allows the manufacturing of identical parts with constant quality.
- Material Flexibility: Cutting-edge CNC machines can handle difficult materials, such as steel alloys and titanium, with less material waste and tool wear.
- 5-Axis Machining: Detailed and multifaceted components can be produced in a single setup using 5-axis CNC machines.
- Advanced Technology Integration: CNC machines can be integrated with robotic systems, additive manufacturing, and laser machining to increase their capabilities and enhance manufacturing processes.
- Automation: CNC technology reduces the amount of manual intervention, which lowers errors and speeds up production without sacrificing quality.
- CAD/CAM Integration: By facilitating smooth transitions from digital models to physical components with exact specifications, CAD/CAM software optimizes the design-to-production workflow.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Through toolpath optimization, reduced manual intervention, and increased production speed, CNC automation shortens machining times.
- Customization and Flexibility: CNC systems facilitate rapid modifications to manufacturing procedures and designs, allowing for the customization of different aircraft models or design revisions.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Cutting forces, temperatures, and tool wear are all tracked by sensors and software installed in sophisticated CNC machines, guaranteeing reliable operation and minimizing downtime.
8. Quality Control and Testing in Landing Gear Machining
Quality control and testing are essential to guaranteeing the dependability and safety of landing gear systems. Here are some quality standards that are crucial to perform in aircraft operations,
- Dimensional Inspections: To ensure dimensional accuracy and compliance, instruments such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are utilized to confirm tight tolerances and geometries in adherence with ASTM F2924 and ASTM E3064.
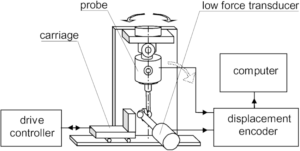
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods include dye penetrant testing (ASTM E1417), radiographic inspection (ASTM E1742), and ultrasonic testing (ASTM E2375) can identify flaws without sacrificing component integrity.
- Material Testing: To make sure components can sustain operational loads, material qualities such as tensile strength and hardness are verified using ASTM E8/E8M for tension testing and ASTM E384 for microhardness testing.
- Functional Testing: To assess durability and performance, landing gear components are put through simulated real-world testing per ASTM F2971.
- Checks for Surface Integrity: ASTM D1005 is used to assess coating thickness, while ASTM B571 is used to test for adhesion and surface finish.
9. Case Study / Real-World Applications of CNC Machining in Landing Gear Mechanisms
The aerospace industry has undergone a revolution through the use of CNC machining in landing gear fabrication, which has improved efficiency, durability, and precision. The following real-world examples exemplify the critical importance of CNC technology:
- Boeing 787 Dreamliner Landing Gear: To manage the titanium and high-strength steel alloys needed for increased load-bearing capacity and decreased weight, the landing gear components for the Boeing 787 are produced utilizing 5-axis CNC machining. During high-impact landings, the safety and dependability of the equipment are guaranteed by CNC's ability to achieve precise tolerances.

- Airbus A350 Hydraulic Actuators: Complex geometries and smooth finishes are achieved through the use of CNC technology. Using the use of CAD/CAM software, Airbus has produced accurate designs that increase hydraulic efficiency and lower operating energy loss.
- Military Fighter Jets (F-35): Landing gear systems for this aircraft must have lightweight parts without sacrificing strength. To ensure longevity in harsh environments, CNC machines are excellent at incorporating factors like shock absorbers and generating complex shapes. ASTM-aligned non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques confirm these components' integrity.

- Mechanisms for NASA's Mars Rover Landing:
CNC machining is used in the production of landing gear mechanics for space exploration vehicles, even though they are not conventional airplanes. These parts demonstrate the adaptability of CNC machining by requiring unmatched precision to operate in alien environments.

10. Future Trend for landing Gear System
Technological, accuracy, and automation developments will determine the future of CNC machining in landing gear manufacturing, to increase productivity, cut expenses, and satisfy the changing needs of aerospace engineering.
- Enhanced Automation and AI Integration:To predict tool wear, improve machining operations in real-time, and minimize human interaction, CNC systems will integrate more machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. This will increase part quality and overall efficiency, especially for intricate landing gear components.
- Hybrid Manufacturing Techniques: More and more additive manufacturing (3D printing) and CNC machining will be combined to produce complex, lightweight landing gear system geometries while cutting lead times and wasteful material usage.
- Innovative 5-Axis and Multi-Axis Machining: As landing gear systems get more complicated, sophisticated 5-axis and multi-axis CNC machines will be essential for creating intricate, high-precision geometries in a single configuration, increasing accuracy and efficiency.a
- Lightweight Materials: The creation of innovative alloys and composites, such as titanium-aluminum intermetallics and carbon fiber-reinforced plastics, will improve fuel efficiency and reduce weight without sacrificing strength.
- Smart Landing Gear: Real-time stress, temperature, and wear monitoring will be possible with the integration of sensors and Internet of Things technologies, improving operating safety and predictive maintenance.
- 3D Printing in Production: Additive manufacturing can help CNC machining by producing intricate, lightweight structures with less wasteful material as well as shorter prototype cycles.

- Electric and Hybrid Actuation Systems: When electric actuators take the place of conventional hydraulic systems, next-generation aircraft will weigh less, use less energy, and require less maintenance.
- Initiatives for Sustainability: To meet the objectives of global sustainability, manufacturers will concentrate on using eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production techniques, and recycling plans.
- Automation of Quality Control: To ensure that parts satisfy exacting aerospace standards in real time, CNC machines will be more frequently combined with in-line inspection systems, such as automated coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) or laser scanners.
- Sustainability in CNC Manufacturing: In line with the aerospace sector's environmental objectives, CNC technology will advance to minimize waste, decrease energy consumption, and encourage the use of eco-friendly materials.
- IoT and Real-Time Data Integration: CNC machines' growing IoT capabilities will make real-time data gathering and monitoring during the machining process possible. By enhancing machine uptime and avoiding production delays, this data will support predictive maintenance.

Conclusion
Landing gear system production certainly has shifted as an outcome of CNC machining, which provides unmatched accuracy, productivity, and flexibility to satisfy the exacting requirements of contemporary aerospace engineering.
The production of landing gear components that guarantee aircraft performance and safety depends heavily on CNC technology because of its capacity to manage intricate geometries, durable materials, and precise tolerances. CNC machining for landing gear systems appears to have an even brighter future as the industry shifts to lighter, more intelligent, and environmentally friendly designs.
AI integration, hybrid manufacturing, and real-time data monitoring are just a few of the innovations that will keep pushing the envelope and ensuring landing gear's continued importance in aviation's development.
CNC machining will remain at the forefront of developing more dependable, effective, and innovative landing gear systems through continued developments. Is this blog helpful for you? If you have any queries let us know by commenting below.