Flange connections are crucial in many machines and structures. They help join two parts together tightly and safely. Using the right flange connection method can make a big difference in industries such as oil, gas, and water. It ensures that everything works smoothly and prevents leaks. Choosing the best way to connect flanges is crucial because it affects safety and efficiency.
Flange Connection Methods
Flange connections connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment. Different methods are used depending on the system's needs. Here, we will examine some widely used methods.
Welded Flange Connections
Welded flange connections are known for their strength and durability. They create a permanent bond between two components, making them ideal for demanding applications. These connections are often used in systems where high pressure or extreme temperatures are present. The strong weld ensures a secure and leak-proof joint. There are two main types:
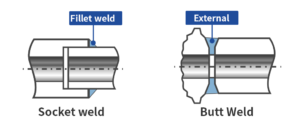
- Socket Weld Flange:
- This flange has a socket where the pipe is inserted.
- Welding is performed on the outer surface of the flange to create a strong connection.
- This type is commonly used for smaller pipes.
- It ensures a solid joint and prevents any fluid from escaping.
- Butt Weld Flange:
- In this method, the pipe is welded directly to the flange.
- The welding is done at the edge, creating a smooth transition.
- This design minimizes turbulence and pressure drops inside the pipe.
Applications:
- High-pressure pipelines that transport liquids or gases.
- Systems that handle hot fluids or gases, such as steam pipelines.
- Power plants and refineries, where reliability is crucial.
Bolted Flange Connections
Bolted flange connections are widely used because they are easy to assemble and disassemble. These connections are not permanent, making them perfect for systems that need regular maintenance or inspection. The primary components of this connection include bolts, gaskets, and nuts.

Key Features:
- Bolts hold the flanges together securely.
- Gaskets act as a cushion between the flanges to prevent leaks.
- Nuts are used to tighten the bolts and maintain a strong grip.
Applications:
- Systems that require frequent repairs or inspections, such as pipelines in industrial plants.
- Water and wastewater treatment facilities, where maintenance is common.
- Chemical processing plants that handle corrosive or hazardous materials.
Threaded Flange Connections
Threaded flange connections are simple and easy to use. These flanges have threads inside their bore, which match the threads on the pipe. This design allows the flange and pipe to screw together without welding. Because of their simplicity, threaded flanges are often used in systems with low pressure and temperature.

Key Features:
- No welding is required, which reduces installation time.
- They are ideal for areas where welding is not feasible, such as flammable environments.
- Threaded flanges can be reused if the system configuration changes.
Applications:
- Low-pressure systems that transport liquids or gases.
- Pipelines operating at lower temperatures.
- Temporary setups are done at construction sites or during repair work.
Lap Joint Flange Connections
Lap joint flanges are unique because they are used in combination with a stub end. The stub end is welded to the pipe, and the flange can rotate around it. This feature makes lap joint flanges easy to align with other flanges during installation. They are especially useful in systems that are dismantled frequently.
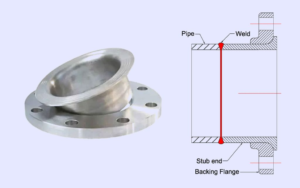
Lap Joint Flange Connections
Key Features:
- The flange can move freely, allowing for quick and easy alignment.
- This design reduces wear and tear on the flange itself, as the stub end bears most of the stress.
- They are commonly used with systems that transport corrosive materials, as the flange can be made from a different material than the stub end.
Applications:
- Systems that require frequent dismantling for cleaning or maintenance.
- Pipelines carrying corrosive or hazardous substances.
- Industrial systems where flexibility is necessary.
Blind Flange Connections
Blind flanges are solid plates designed to close off the end of a pipe or system. Unlike other flange types, they do not have a bore for fluid or gas flow. Instead, they create a complete seal, making them ideal for isolating system parts or performing pressure tests.

Blind Flange Connections
Key Features:
- They provide a strong and reliable seal to block flow completely.
- Blind flanges can handle high pressure and are often used in testing applications.
- They are available in various materials to match the requirements of the system.
Applications:
- Temporary closures during maintenance or upgrades.
- Permanent end caps for pipelines that are no longer in use.
- Systems that require pressure testing before becoming operational.
Pros and Cons of Each Flange Connection Method

Welded Flange Connections
Pros:
- Strong and reliable for high-pressure systems.
- Works well in extreme temperatures.
- Prevents leaks with a solid weld.
Cons:
- Installation takes time and skill.
- Once welded, it is not easy to remove.
- Repairs can be costly if something goes wrong.
Bolted Flange Connections
Pros:
- Easy to install and remove.
- Ideal for systems that need frequent maintenance.
- Components like bolts and gaskets are replaceable.
Cons:
- Gaskets can wear out over time.
- Bolts may loosen under vibration.
- Not as strong as welded connections in high-pressure settings.
Threaded Flange Connections
Pros:
- Quick and easy to install.
- No need for welding or special tools.
- Perfect for portable or temporary systems.
Cons:
- Limited to low-pressure and low-temperature systems.
- Threads can wear out over time.
- Not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Lap Joint Flange Connections
Pros:
- Flexible and easy to align during installation.
- Suitable for systems that need frequent dismantling.
- Reduces wear on the flange because the stub end takes most of the stress.
Cons:
- Not as strong as welded or bolted connections.
- More expensive due to the need for a stub end.
- May not seal as tightly as other methods.
Blind Flange Connections
Pros:
- Provides a strong and reliable seal.
- Ideal for isolating or testing systems.
- Works for both temporary and permanent closures.
Cons:
- Not designed for flow; it completely blocks the pipe.
- Removal requires stopping the entire system.
- Not suitable for systems needing regular access.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Flange Connection Method
When picking a flange connection method, it's important to consider several factors. These factors will help you decide the most appropriate method for your needs. Let's take a look at what factors to consider.

Flange Connection MethodFlange Connection Method
1. System Requirements
Pressure and Temperature:
- High-pressure systems need strong connections like welded flanges.
- Low-pressure systems can use threaded or lap joint flanges.
Temperature:
- High temperatures require durable connections like welded flanges.
- Lower temperatures allow for more flexible options like bolted or threaded flanges.
2. Maintenance and Accessibility
Frequency of Maintenance:
- If the system needs regular checks, bolted flanges are suitable because they are easy to open and close.
- Systems that don't need frequent maintenance might use welded flanges since they don't need to be opened often.
Ease of Access:
- Consider how easy it is to reach the flange.
- Bolted and lap joint flanges are easier to handle if access is limited.
3. Safety and Reliability
Leak Prevention:
- A tight seal is crucial. Welded flanges offer the best leak protection.
- Gasket quality in bolted flanges also affects leak prevention.
Strength and Durability:
- Choose a connection that can handle the stress and strain in your system.
- Welded flanges are robust and durable.
4. Cost Considerations
Initial Cost:
- Welded flanges and lap joint flanges can be more expensive upfront.
- Bolted and threaded flanges might be cheaper initially.
Long-Term Costs:
- Think about future repairs or replacements.
- Due to worn-out parts, such as gaskets and bolts, bolted flanges might have higher maintenance costs.
5. Installation Requirements
Tools and Skills Needed:
- Welded flanges need skilled workers and special tools for installation.
- Bolted and threaded flanges are easier to install with basic tools.
Time for Installation:
- Some methods take longer to install. Welded flanges take more time than bolted or threaded flanges.
- Consider how much time you have for installation.
Conclusion
Flange connections are essential in various industries. The choice of the appropriate method relies on considerations such as pressure, temperature, maintenance, and cost. Welded flanges are strong and reliable for systems with high pressure. Bolted flanges are easy to maintain and replace. Threaded flanges work well for low-pressure and portable setups. Lap joint flanges offer flexibility, and blind flanges are perfect for sealing systems.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. It's essential to evaluate the specific needs of your system before making a choice. Selecting the appropriate option ensures safety, reduces leaks, and improves efficiency. The right flange connection will help your system operate effectively for an extended period.






