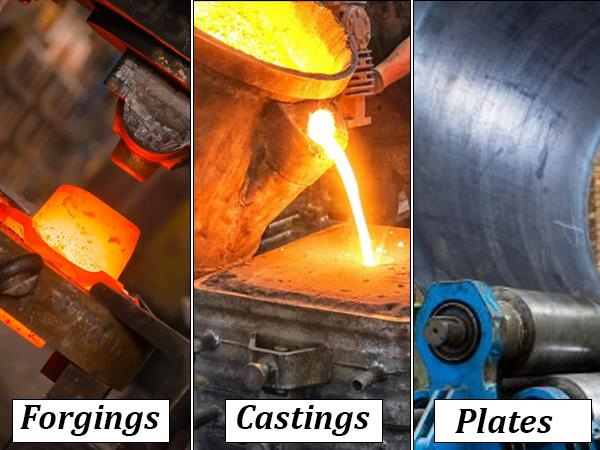
Do you want to know which blank material is best for modern manufacturing? Oh yes! But understanding forgings, castings, and plates can feel tricky. Don’t worry! Each type has its own strengths and uses that make it special.
In this article, you will learn how forgings, castings, and plate materials are made and used. Also, you will learn their key differences and benefits. Hence, you will know how to choose the right blank for your project.
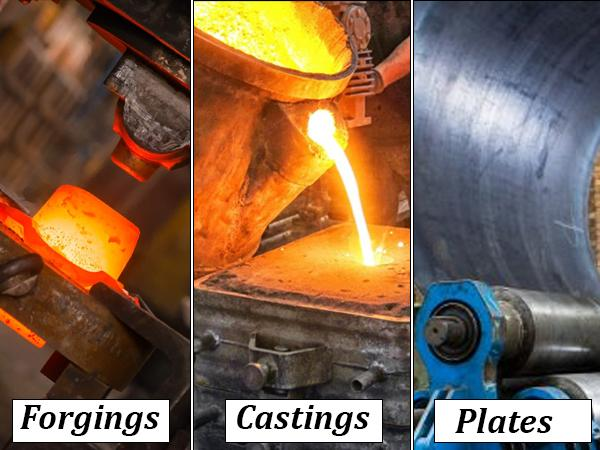

Figure 1: Forgings vs Castings vs Plate Materials
1) Overview of Blank Material Types
First of all, in factories, workers make parts from different types of metal pieces. These pieces of metal are called blanks. So, the way the blank is made and the changes in the blank. For example, how strong or expensive the final part is. There are three main types of blanks:
- First of all, forgings are made by heating metal and pressing it strongly. So this makes the metal very strong and hard.
- Next, castings are made by melting the metal and pouring it into a mold. As well, when the metal cools. Then it takes the shape of the mold. So this method is best for parts that have difficult shapes.
- Then, plates are made by rolling the metal into flat sheets. Then these sheets can be easily cut and shaped. So you can create straight or smooth parts. For example, lids or bases.
Hence, forgings create strong parts. Then the castings help create complex shapes. And plates are great for making simple and cheap flat objects. So each method is beneficial for its own purpose.
2) Forgings: Strength Through Deformation
As you learn about the overview of blank material types. Now you will learn about forging and its types. So, forging is a process in which metal is heated. And then pressed into a new shape. Moreover, this work is done with the help of large hammers or heavy machines.
Also, the goal is to improve the direction of the metal. So your metal becomes stronger. Therefore, forging is used in industries where strength and safety are important. So you commonly use it in aircraft manufacturing, automobiles, and heavy machinery.
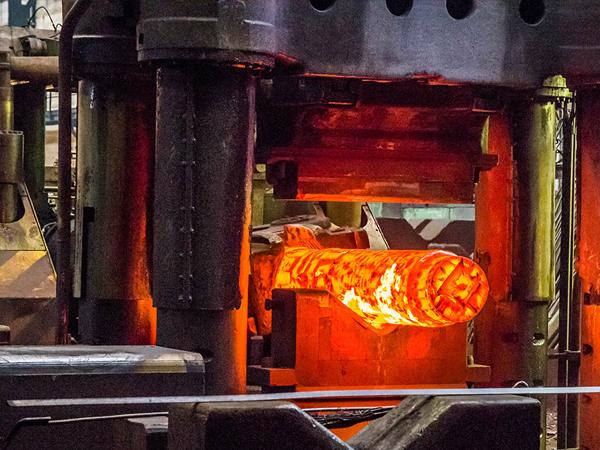

Figure 2: Forgings
For example, aircraft landing gears, car axles, and industrial shafts are made from forging. Also, there are three main types of forging:
i) Open-Die Forging: First of all, in this method, you press the metal between two open molds. Also, you use this method to make large and simple shapes, such as shafts or discs.
So this method improves the strength and longevity of your metal. Because it maintains the correct direction of your matel.
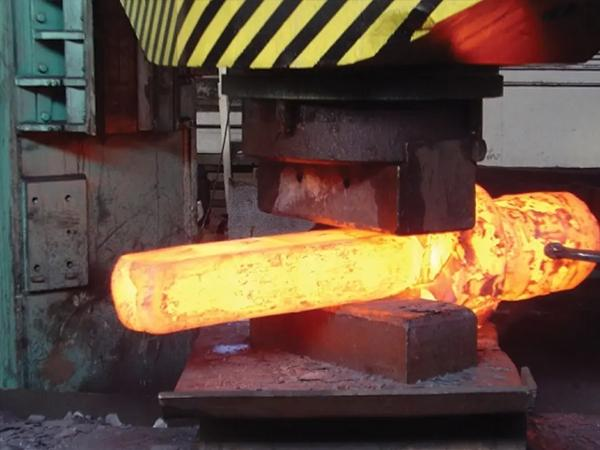

Figure 3: Open-die Forging
ii) Closed-Die Forging: Next, in this method, you place the metal in a closed mold that completely covers it. So when you applied pressure. Then the metal fills the whole mold and takes its exact shape. Moreover, you use this method to make small and thin parts. Also, you use it to make tools, gears, and automotive parts.
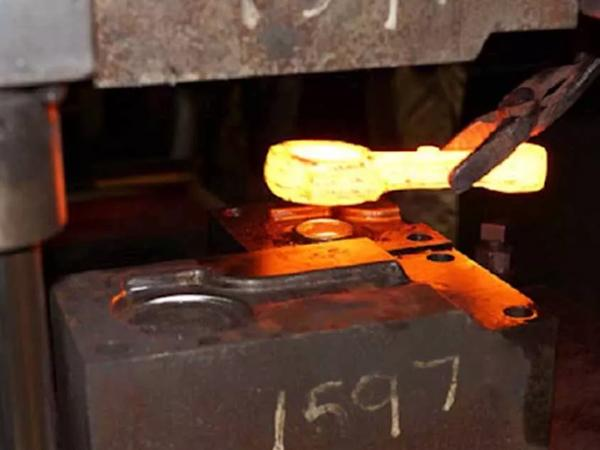

Figure 4: Closed-die Forging
iii) Drop Forging: Then, in drop forging, you heavily fall a hammer on the hot metal. Then each blow forces the metal into the mold. So, this process makes your metal much stronger and more shock-resistant. Also, you use this method for parts that are subject to high stress or shock. For example, crankshafts and connecting rods.
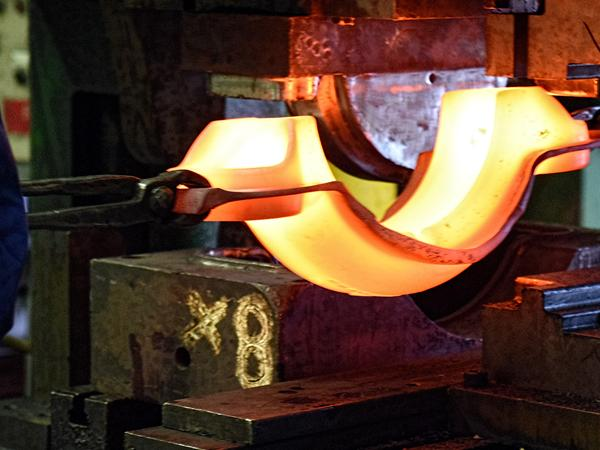

Figure 5: Drop Forging
➢ Pros and Cons of Forging
| Pros | Cons |
| Very strong metal | Needs big machines |
| Lasts a long time | Hard to shape |
| Smooth grain inside | Takes more time |
| Can bear a heavy load | Costs more money |
| No cracks inside | Not for hollow parts |
3) Castings: Complexity Through Molding
As you learn about the forgings and their types. Now you will learn the castings and their types. So casting is a process in which you molten metal. Then you poured it into a mold to obtain a specific shape. As well, when the metal cools. Then you harden and take the shape of the mold.
So you use this method for parts that have complex or delicate shapes. Also, you use castings in industries where it is necessary to produce more parts in a shorter period of time. For example, you can use it in engine parts, machinery, and pumps. Also, there are three main types of castings:
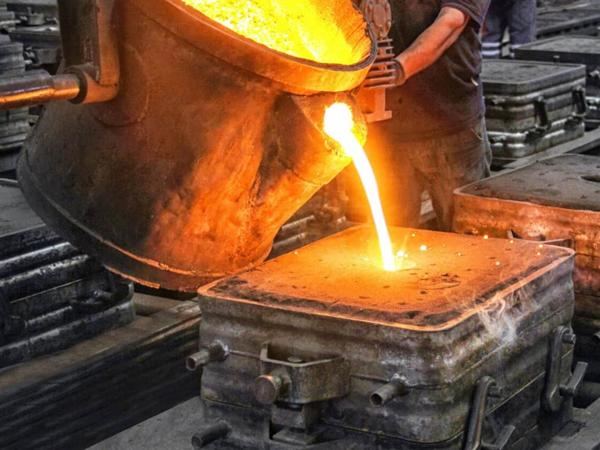

Figure 6: Castings
i) Sand Casting: First of all, in sand casting, you pour the metal into a sand mold. So you can use this method for making large and heavy parts. Also, sand molds are easy and cheap to make. But the surface is not very smooth.
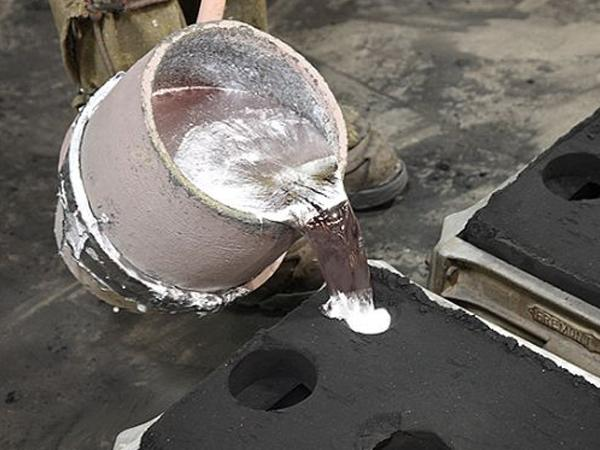

Figure 7: Sand Casting
ii) Investment Casting: Next, in this method, you make a wax model. Then you covered it with a ceramic material. As well, when you heat it. Then the wax melts and the metal is filled in its place. So you use this method for making small and smooth parts. For example, tools, jewelry, and aircraft parts.
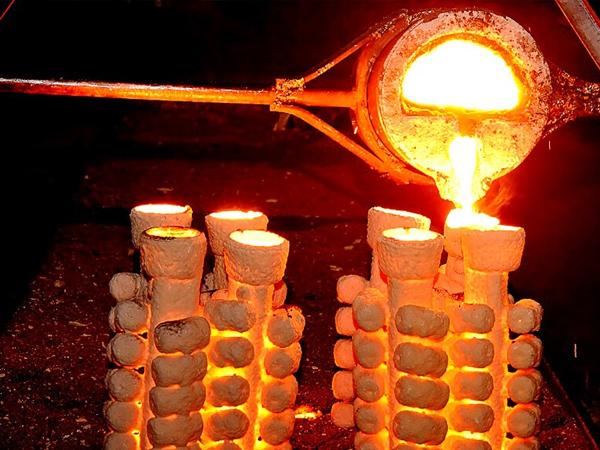

Figure 8: Investment Casting
iii) Die Casting: Then, in die casting, you use metal molds. So you fill the molten metal into the mold under high pressure. Also, you use this method for making many identical parts quickly and accurately. For example, car parts, housings, and small machine parts.
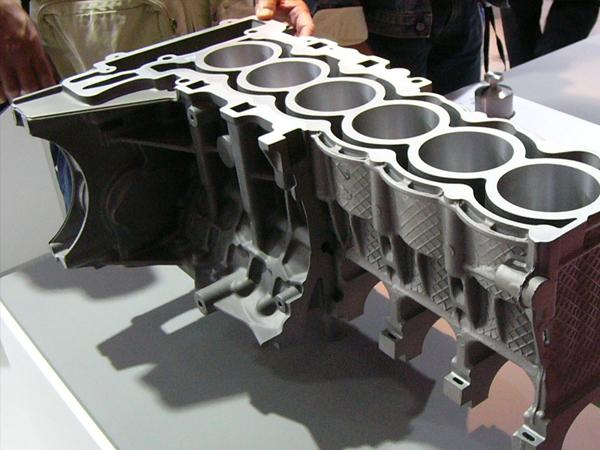
Figure 9: Die Casting
➢ Pros and Cons of Casting
| Pros | Cons |
| Makes complex shapes | May have small holes |
| Works with many metals | Lower strength level |
| Good for mass production | Hard to inspect inside |
| Smooth surface finish | Can have weak spots |
| Low production cost | Not for high-stress parts |
4) Plate Materials: Precision Through Rolling
As you learn about the castings and their types. Now you will learn plate materials and their types. Moreover, plate materials are large, flat sheets of metal. Also, you make them by rolling thick pieces of metal. So rolling makes the surface of the metal smooth and uniform in thickness. There are two main types of plates.
i) Hot-rolled plate
First of all, in this process, you heat the metal to a high temperature. Then you flattened and thinned it by passing it through heavy rollers. Moreover, hot rolling is a faster and less costly process. And also, it is better for thicker plates. However, the surface of these plates is rougher and less accurate. So you can use it in construction and heavy machinery.
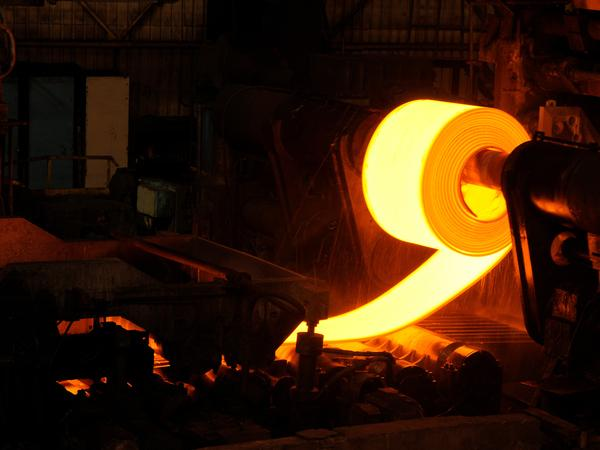

Figure 10: Hot-rolled plate
ii) Cold-rolled plate
Next, in this method, you do not heat the metal. Rather, you rolled it at room temperature. So this makes your metal surface shiny and accurate in size. Moreover, you use cold-rolled plates in places where beauty and accuracy are essential. For example, you use this method in automobiles and household appliances.
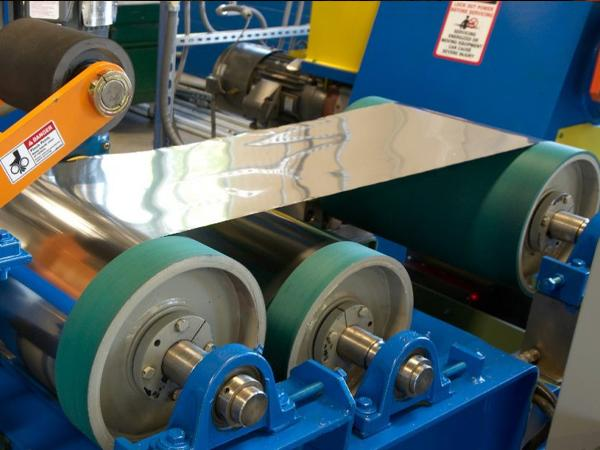

Figure 11: Cold-rolled plate
➢ Pros and Cons of Plte Material
| Pros | Cons |
| Uniform thickness | Not for complex parts |
| Smooth surface | Can bend under pressure |
| Easy to cut and shape | Slightly higher cost |
| Good for flat parts | Limited shape options |
5) Detailed Comparison: Forgings vs Castings vs Plate Materials
As you learn about the plate materials and their types. Now you will learn the comparison in detail between Forgings vs Castings, vs Plate Materials.
| Criteria | Forgings | Castings | Plate Materials |
| Manufacturing Process | Deformation | Melting & Molding | Rolling & Cutting |
| Strength & Toughness | High | Moderate | Medium |
| Shape Complexity | Limited | High | Low |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Moderate | High | High |
| Defect Risk | Low | Moderate to High | Low |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate | Lower |
| Applications | High-stress parts | Complex shapes | Flat components |
6) Key Factors in Blank Selection
As you learn the comparison in detail between Forgings vs Castings, vs Plate Materials. Now you will learn the factors in blank selection.
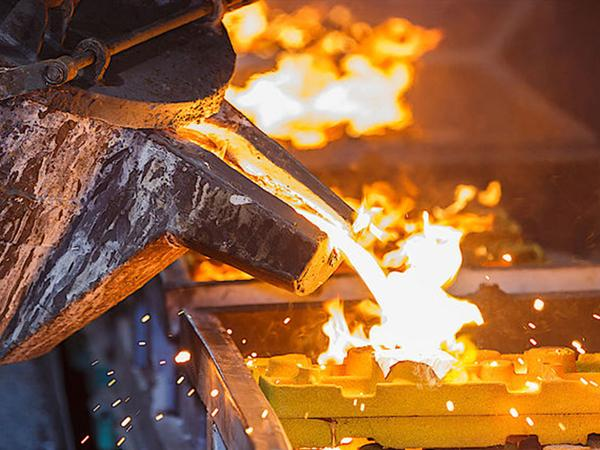

Figure 12: Key Factors in Blank Selection
i) Strength and Durability
First of all, every blank has a different strength. Moreover, forging is generally 20 to 30 percent stronger than casting. Because the metal grains within it conform to the shape of the part. So this makes your metal stronger and resistant to breakage.
Also, castings are weak but sufficient for general use. On the other hand, plate material gives you medium strength. Also, its properties remain consistent
ii) Shape Complexity
Next, the shape plays an important role in the selection of the blank. So forging is better for your simple and strong parts. For example, shafts or rings. On the other hand, casting is suitable for your complex shapes. For example, engine blocks or pump bodies. Then the plates are best for making your flat parts. For example, covers, flanges, or brackets.
iii) Production volume and cost
Then, if you are making parts in small quantities (fewer than 500 units). For that, forging is a better choice for you. Because every part is stronger. But if you are producing in large quantities. Then, you chose castings or plates that are cheaper per part.
As well, casting molds and dies are costly. On the other hand, the cost is spread over large production runs. So, plates are the lowest-cost solution for your low-stress jobs.
iv) Material Availability
After that, availability depends on the metal type and market. For example, carbon steel plates are common and easily available. On the other hand, forging-grade alloy steels can take time to obtain.
Then, in casting, you can use different metals. For example, aluminum, bronze, or cast iron. So having materials readily available locally saves your time and cost.
v) Machinability
Moreover, machinability refers to how easy it is to cut or shape a metal. So plates have excellent machining properties. Because they have a smooth surface. On the other hand, forgings are harder. So machining can be difficult.
Then, castings are different; aluminum is easily machined. So, iron castings need stronger tools. Hence, better machinability reduces time and tooling costs.
vi) Safety Standards
Afterward, international standards such as ASTM, ASME, and ISO set safety rules for every industry. For example, forged parts are essential in the aerospace and oil industries. Because they withstand high stress.
On the other hand, casting parts need X-ray inspection to confirm there are no internal defects. So, structural steel codes must be met for the construction plates.
vii) Thermal Resistance
Furthermore, if your part will be exposed to high heat. Then you choose the blank carefully. Moreover, forged steel can withstand up to 600°C. On the other hand, cast aluminum becomes weak after 300°C. Therefore, stainless steel or nickel alloy plates can also withstand higher temperatures. But only in simple shapes.
viii) Corrosion Resistance
At last, metal can be damaged by moisture or chemicals. So stainless steel plates or bronze castings are good candidates for resistance to corrosion. On the other hand, forged carbon steel often needs coating or heat treatment. So you always choose a material for your environment. For example, marine, chemical, or outdoor use.
Conclusion
In short, your products perform better when you choose the right blank. Moreover, forgings give you more strength. On the other hand, you use casting to make complex shapes easily. Then, you use plates for simple and flat designs.
Hence, every type has its own use. Therefore, you always choose the blank according to the needs of your project. So, this way you get better quality and smoother production.






